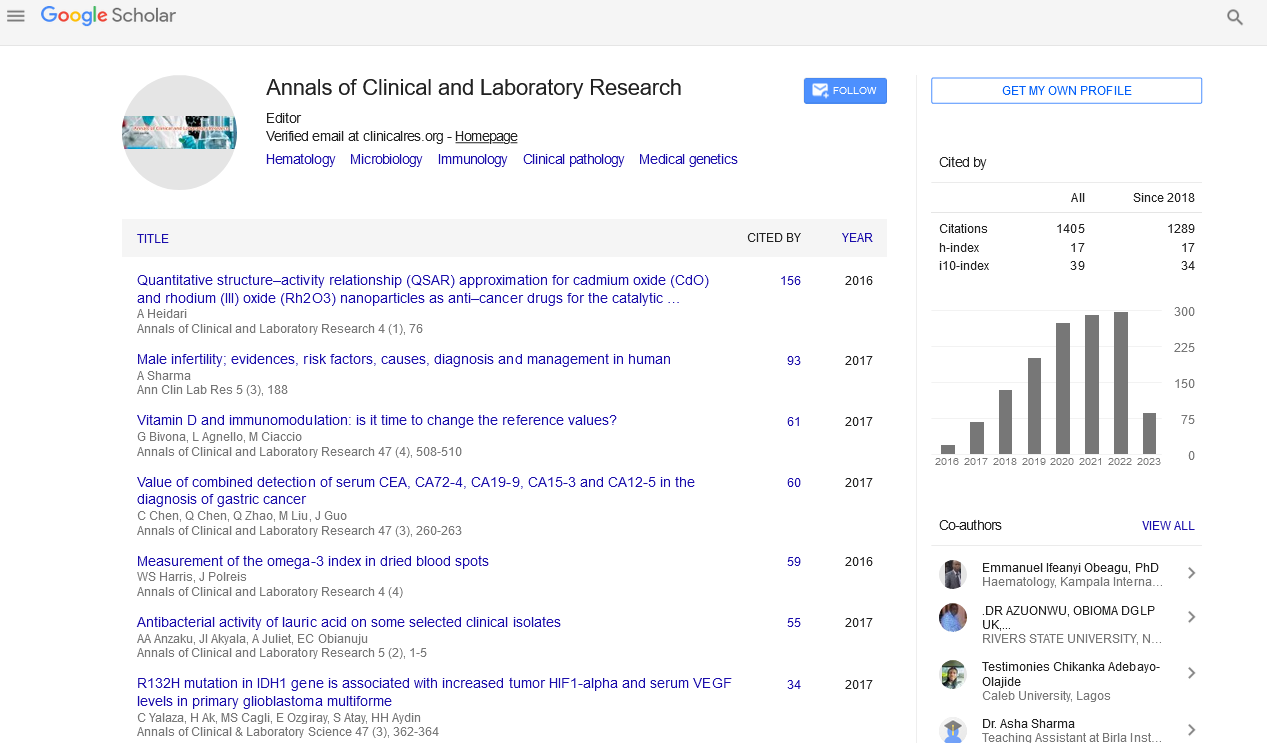
Rapid Communication - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 3
Cancer Uncovered Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Advance Essential Growth Development by means of IL6
Maureen Blacher*
1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Domaine Universitaire, Belgium
*Correspondence:
Maureen Blacher, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Domaine Universitaire,
4000 Liège,
Belgium,
Email:
Received: 01-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. IPACLR-22-400;
Editor assigned: 03-Feb-2022, Pre QC No. IPACLR-22-400(PQ);
Reviewed: 18-Feb-2022, QC No. IPACLR-22-400;
Revised: 22-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. IPACLR-22-400(R);
Published:
01-Mar-2022, DOI: 10.36648/2386-5180.22.10.400
Abstract
The growth microenvironment (TME) is a perplexing biological system comprising of disease cells, extracellular framework and non-disease stromal cells (invulnerable, provocative, endothelial cells and fibroblasts). It is presently very much perceived that the perplexing crosstalk laid out between disease cells and stromal cells effectively adds to cancer movement and metastatic dispersal that can happen through blood as well as lymphatic. Lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) lining introductory vessels are upheld by a broken storm cellar film and associated by "button-like" between endothelial adherens intersections shaped, by homotopic communications of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cad). These particular intermittent intersections could work with the take-up of interstitial liquid and (invulnerable and disease) cells, two vital elements of introductory lymphatic vessels (LV).
Keywords
Microenvironment, Lymphatic vessels, Cadherin
Introduction
Inside the TME, LEC answer development factors (chiefly vascular endothelial development factors: VEGF-A/C) and add to a significant LV rebuilding and the arrangement of new LV from previous ones. This course of lymphangiogenesis connects with lymph hub (LN) metastasis and more unfortunate clinical result. After a long discussion in mainstream researchers, exploratory mouse model examinations exhibited that metastatic cells in sentinel LN can additionally spread to far off organs by getting to particular high endothelial venules (HEV). As well as giving a course to cancer cell spreading, LV additionally impact hostile to growth insusceptibility in essential cancer and in depleting LN. The intricate interaction among LEC and the insusceptible framework in explaining an immunosuppressive TME has as of late arisen [1]. Progresses in this field have featured LEC suggestion in insusceptible cell enlistment/dealing and in immunosuppression through various components that incorporate, the creation of PDL-1 advancing CD8+ T cell tolerization and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) prompting tryptophane erasure and hindrance of T cell capacities. LEC show up progressively as a heterogeneous cell populace as far as sub-atomic and underlying highlights, which show versatile limits. The ramifications of LEC versatility in the TME and how it very well may be involved during malignant growth movement and metastatic spread remains inadequately archived [2]. In essential cancers, peritumoral LV are many times amplified and considered as the significant course for dispersal. In the inverse, intratumoral LV seem imploded because of the growth pressure and are seen as unfunctional and insignificant in the TME. These perceptions bring up issues on LEC inclusion in the development of TME during disease movement.
During the last many years, lymphatic examination has chiefly centered around sub-atomic components driving lymphangiogenesis and how LV add to cancer and invulnerable cell dealing prompting an immunosuppressive TME and metastatic colonization in LN in far off organs. LEC-inferred chemokines drive growth cell movement towards LV and direct cancer cell-LEC contacts advance melanoma cell intravasation and attack. Growth cells can likewise disturb intercellular connections between LEC shaping holes in the lymphatic divider that act as passage destinations for cancer cells in lymphatic vessels to arrive at lymph hubs. This "vascular driven view" is dismissing putative jobs of LEC in the TME that are a long ways past their LV coating capacities and favorable to metastatic impacts. We here hypothesize that LEC could apply different consequences for cancer cells and growth movement that are free on their ability to frame a vascular divider. We estimated that LEC presented to growth cells (teLEC) can be invigorated to deliver favorable to tumorigenic factors and thusly be dynamic stromal players in the complex TME. To resolve this issue, we utilized the HaCaT model of skin squamous cell carcinoma showing elements of cancer movement from harmless (HaCaT cells) to second rate dangerous (HaCaT-II-4 cells) and metastatic (HaCaT-A5-RT3 cells) growths [3]. The awareness of these cells to factors got from initiated stromal cells (fibroblasts) is all around reported. We exhibit that growth cells disturb LEC monolayer honesty and initiate a phenotypic switch in teLEC, which thus advances disease cell expansion and movement. Robotically, we give in vivo proof that IL6-got from teLEC advances malignant growth cell multiplication list that is impeded by killing enemy of IL6 counter acting agent. We are doling out an original capacity to teLEC, which act as a novel stromal wellspring of controllers of growth cell expansion in the TME.
A potential motivation behind why hypertension control rates for cardiology patients don't seem, by all accounts, to be ideal might be that cardiologists think about hypertension as an essential consideration condition. Keeping in mind the job of the essential consideration professional and with a sharp aversion to the conceivable view of the expert's assuming control over the whole consideration of the patient, cardiologists might be unwilling to start or change hypertension treatment.
A subsequent conceivable justification for why control rates have not worked on over the long haul might be that hypertension has been swarmed out as a focal point of remedial endeavours in something like 3 ways. To begin with, in a populace of patients who are ordinarily more established and more broken down, other intense and constant issues, like hypotension and renal disappointment, may muddle the clinical picture and make the board of hypertension really testing [4]. Second, in a populace of persistently and seriously sick patients, different subject matter experts, like nephrologists, might be taken care of hypertension. Third, on-going advances in therapeutics have been gathered in regions other than hypertension. Inside the beyond quite a long while, novel methodologies have opened up in cholesterol the board, anticoagulation treatment, and cardiovascular breakdown, yet there have been no new blockbuster treatments for hypertension that stand out enough to be noticed [5].
REFERENCES
- Miteva DO, Rutkowski JM, Dixon JB, Kilarski W, Shields JD, et al. (2010) Transmural flow modulates cell and fluid transport functions of lymphatic endothelium. Circ Res 106: 920-931.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Masjedi A, Hashemi V, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Ghalamfarsa G, Azizi G, et al. (2018) The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 108: 1415-1424.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Maillard C, Jost M, Rømer MU, Brunner N, Houard X, et al. (2002) Host plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promotes human skin carcinoma progression in a stage-dependent manner. Neoplasia 7: 57-66.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Taher MY, Davies DM, Maher J (2018) The role of the interleukin (IL)-6/IL-6 receptor axis in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans 46: 1449-1462.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Biffi G, Oni TE, Spielman B, Hao Y, Elyada E, et al. (2019) Il1-induced Jak/STAT signaling is antagonized by TGFβ to shape CAF heterogeneity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Canc Discov 9: 282-301.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Citation: Blacher M (2022) Cancer Uncovered Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Advance Essential Growth Development by means of IL6. Ann Clin Lab Res. Vol.10
No.3:400