Keywords
Cardiotonic activity, digoxin, Aegle marmelos, isolated frog heart
Introduction
Herbs and preparations thereof have been used to treat ailments since medicine began. The treatment of diseases with medicines of plant origin is an integral part of many cultures throughout the world. Now a days 80% of the world’s population uses medicines, which are directly or indirectly derived from plants. Worldwide, such medicines make up a 25% share of the pharmaceutical arsenal. Based on the strong traditional knowledge on the use of plants as therapeutic agents, a rational approach is being developed to use the medicinal plants as lead for the discovery of active molecules. The essential organ of the human body i.e. heart when fails to work leads to sudden death. Since the potent cardiotonic drug i.e. the digoxin which is of the plant origin has a long list of ADR and toxicity, it is a need of hour to develop and standardise cardiotonic drugs of herbal origin. [1-8]
Aegle marmelos (L.) (Rutaceae) commonly known as bael or koovalam (Malyalam, India) growing wildly throughout deciduous forest of India, ascending to an altitude of 1,200 m in western Himalayas and also occurring in Andaman Islands. The fruits and leaves are valued in indigenous medicine. The plant has been employed for long time in folk therapy. Poultice made of leaves is used for ophthalmia and ulcers. The leaves are used to reduce blood glucose level. Other actions like antifungal, antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, antidiarrhoetic, pesticidal, antidote, anti-inflammatory properties, antispermatogenic has been reported. Certain biochemical constituents namely alkaloids, Aegleinol, coumarin, steroid, terpenoid and tannins, Dglucoside, marmesinine, lupeol, tannins, phlobatannins, flavonoids, umbelliferone, quercetin and volatile oils (Eugenol and methyl eugenol) are reported in different parts of the tree. It has been reported that leaves possess cardiotonic, antiasthmatic, antifungal, analgesic and antioxidant activities. Since there was no report in literature regarding the cardiotonic activity of A. marmelos fruits. We decided to determine the same with the help of isolated frog heart assembly. [9-10]
Experimental Work Done
Materials and methods [12]
Drug : Juice of Aegle marmelos fruits
Chemicals : Digoxin, Ringer Solution
Animals : Frog of Rana tigrina species were used for the study and those were maintained as per CPCSEA guidelines.
Instruments: Sherington Rotating Drum, Sterling’s heart lever
1. Preparation of juice
The fresh fruits of Aegle marmelos ( Bael ) of Family Rutaceae were collected from Manchar, Tal. Ambegaon, Dist. Pune and authenticated at Botanical Survey of India, Koregaon Park, Pune. One specimen was preserved in Department of Pharmacognosy of our institute for the reference. The fruits were washed thoroughly to remove adhered material. Seeds were separated from the fruit, pulp was mixed with distilled water thoroughlyinmixer .The materialwas filtered throughWhatman filter paper no.40 and filtrate was collected .The prepared juice was diluted with the help of distilled water in varying proportion and labeled as follows,
A1-Undiluted filtrate
A2-1:1 (filtrate: distilled water)
A3-1:2 (filtrate: distilled water)
A4-1:4 (filtrate: distilled water)
All the preparations were evaluated for their cardiotonic activity by using isolated frog heart assembly. The rate and force of heart contraction was determined.
2. Preparation of digoxin solution
The marketed digoxin ampoules (Sunpharma Ltd.) were obtained from local market. Various different dilutions were made with distilled water and labeled as follows, B1- 25 µg/ml, B2- 50 µg/ml. Above prepared samples were evaluated for their cardiotonic activity and treated as standard.
3. Preparation of hypodynamic ringer solution [14]
Hypodynamic ringer solution was prepared by using standard method (Table-1)
| Sr. No. |
Ingredients |
Quantity |
| 1. |
Sodium chloride (NaCl) |
6.5 gm |
| 2 |
Potassium chloride (KCl) |
0.14 gm |
| 3 |
Calcium Chloride (CaCl2) |
0.03 gm |
| 4 |
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) |
0.2 gm |
| 5 |
Glucose |
2 gm |
| 6 |
Distilled Water |
1000 ml |
Table 1: Composition of Hypodynamic ringer solution
Evaluation of cardiotonic activity [17]
The frog of species Rana tigrina was pithed and pinned it to the frog board. A midline incision was given on the abdomen, the pectoral girdle was removed and the heart was exposed. The pericardium was carefully removed and put a few drops of hypodynamic frog ringer over the heart. The inferior venacava was traced, put a thread around it and given a small cut in order to insert the venous cannula. The cannula was inserted in the vein and the thread was tied to assure the cannula in place which is in turn connected to a saline bottle containing hypodynamic frog ringer solution. A small cut in one of the aorta was given for the ringer to come out. Heart was isolated and attached to the stand with moderate flow of ringer. A thin pin hook was passed through the tip of the ventricle and with the help of a fine thread attached to the hook; it was tied to the free limb of the Sterling’s heart lever which was fixed to a stand. A proper tension was adjusted by altering the height of the lever. The normal heart rate was noted. All test samples that is A1, A2, A3, A4, B1 and B2 were administered in different doses viz. 0.1ml, 0.2ml, 0.3ml respectively. The rate and force of heart contraction were noted as given in (Table 2-7, Figure 1- 7).
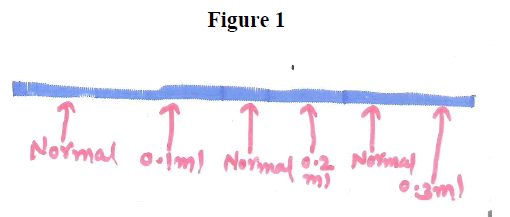
Figure 1
| Sr. No. |
Drug |
Dose(in ml) |
Beats/min. |
Change in Force |
| 1 |
..... |
Normal |
33 |
Normal |
| 2 |
A1 |
0.1 |
32 |
Rapid Increase |
| 3 |
A1 |
0.2 |
29 |
Slight Increase |
| 4 |
A1 |
0.3 |
31 |
No Change |
Table 2
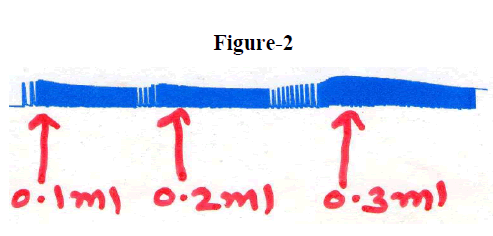
Figure 2
| Sr. No. |
Drug |
Dose (in ml) |
Beats/min. |
Change in Force |
| 1 |
..... |
Normal |
37 |
Normal |
| 2 |
A2 |
0.1 |
34 |
Increase |
| 3 |
A2 |
0.2 |
24 |
Increase |
| 4 |
A2 |
0.3 |
29 |
RapidIncrease |
Table-3
Figure 3
| Sr.No. |
Drug |
Dose (in ml) |
Beats/min. |
Change in Force |
| 1 |
..... |
Normal |
32 |
Normal |
| 2 |
A3 |
0.1 |
29 |
RapidIncrease |
| 3 |
A3 |
0.2 |
27 |
Increase |
| 4 |
A3 |
0.3 |
28 |
Increase |
Figure 4
Figure 4
Sr.
No. |
Drug |
Dose (in ml) |
Beats/min. |
Change in Force |
| 1 |
..... |
Normal |
26 |
Normal |
| 2 |
A4 |
0.1 |
24 |
No change |
| 3 |
A4 |
0.2 |
27 |
No change |
| 4 |
A4 |
0.3 |
28 |
No change |
Table 5
Figure 5
| Sr. No. |
Drug |
Dose (in ml) |
Beats/min. |
Change in Force |
| 1 |
..... |
Normal |
28 |
Normal |
| 2 |
B1 |
0.1 |
23 |
Increase |
| 3 |
B1 |
0.2 |
22 |
Slight
decrease |
| 4 |
B1 |
0.3 |
24 |
Increase |
Table-6
Figure 6
Sr.
No. |
Drug |
Dose (in ml) |
Beats/min. |
Change in Force |
| 1 |
..... |
Normal |
30 |
Normal |
| 2 |
B2 |
0.1 |
27 |
Increase |
| 3 |
B2 |
0.2 |
26 |
Slight Increase |
| 4 |
B2 |
0.3 |
20 |
Sudden
Cardiac Block |
Table 7
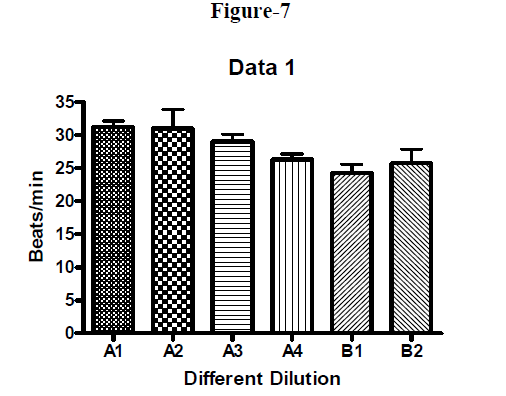
Figure 7
Observations
Results and Discussion
All the dilutions of Aegle marmelos (Bael) restore cardiac activity of Hypodynamic frog heart i.e. it increases rapidity and force of contraction. It was found that sample A3- 1:2 (filtrate: distilled water) showed better response as compared to other samples. It is interesting to know that Aegle marmelos (Bael) has rapid onset of action compared to Digoxin. These preliminary studies confirm the better cardiotonic activity of Aegle marmelos (Bael), and it can stand as better option for digitalis. Further studies can confirm the reduced toxicity & this will be the advantage of Aegle marmelos (Bael) over digitalis. Thus, in future it will be interesting to isolate the active chemical constituents which are responsible for the cardiotonic activity as well as to determine the possible mechanism of action.
Conflict of Interest: NIL.
Source of Support: NONE
5471
References
- Emilio L. Ghisalberti, Survey of Secondary Plant Metabolites with Cardiovascular activity, Pharmaceutical Biology, Volume- 36, Issue-4 October 1998:237-279.
- Stephen CP, Aaron H, Herb drug interactions and compounding in clinical trial, J Herb Pharmacotherapy, 2(1)2002, 23-36.
- Harsh Mohan - Textbook of Pathophysiology, 4th edition 2000, Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: 278-325.
- Goodman & Gillman, The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 9th edition 1996, McGraw Hill Publications: 810-820.
- Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, 19th Edition, Mack Publishing Company: 956.
- Tripathi KD, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 5th Edition 2003, Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers, New Delhi: 457-467.
- Barar FSK, Essentials of Pharmacotherapeutics, 1st edition 1985, S.Chand Publications: 253, 254.
- Satoskar RS, Bhandarkar SD, Ainpure SS, Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics,16th Edition 1997, Popular Prakashan, Mumbai: 352-355.
- Nadkarni AK, The Indian Materia Medica, Popular prakashan 2nd edition: 45
- Anonymous, The Wealth of India, Aegle marmelos (Bael), Supplement series Raw Materials, Part-1st , A Dictionary of Indian Raw Materials and Industrial Products, Council of Scientific Industrial Research (New Delhi), 26-27.
- Terence JC and Peter SM, Digoxin in heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias, MJA 2003; 179 (2): 98- 102.
- Tare HL and Thube BB, Cardiotonic activity of Cassia angustifolia with digoxin on perfused frog heart, IJPRD, Vol 1(1): 1-14.
- Ansari KU, Gupta N, Bapat SK, Frusemide-Digitalis Interaction on Experimental model,IJMS (47) Dec1993:277-279.
- Kulkarni SK, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 2nd Edition 1993, Vallabh Prakashan: 9, 74-76.
- Kale SR & Kale RR, Practical Pharmacology and toxicology, 6th edition 2003 Nirali Prakashan: 27, 28