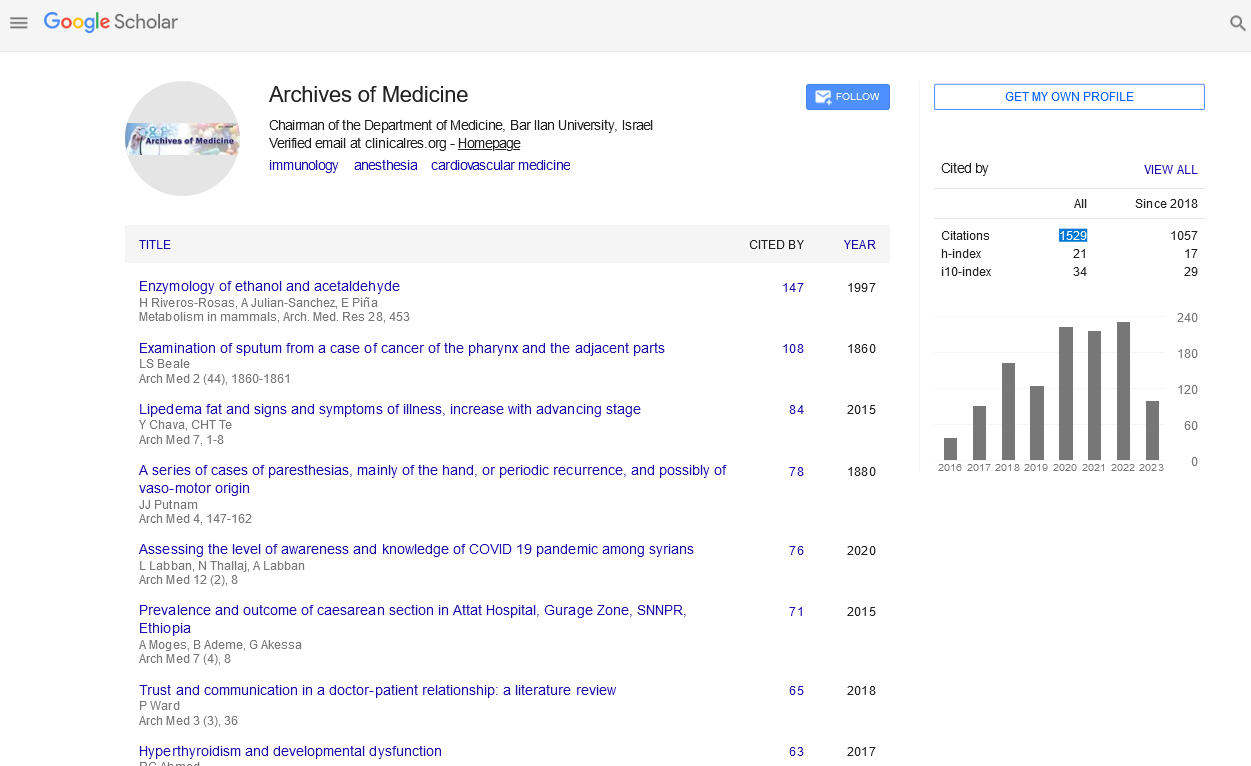
Omer Salah Mirghani Makawi*, Bassam Adil, Mohammed Daghash, Mohammed Al-Awad and Mohammed Shakeeb
Department of Internal Medicine, Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qatar
- *Corresponding Author:
- Omer Salah Mirghani Makawi
Department of Internal Medicine
Hamad Medical Corporation
Doha, Qatar
E-mail: omersalah3475@gmail.com
Received Date: December 09, 2021; Accepted Date: December 15, 2021; Published Date: December 22, 2021
Citation: Makawi OSM, Adil B, Daghash M, Al-Awad M, Shakeeb M (2021) Complicated Intramuscular Tuberculous Cold Abscess. Arch Med Vol.13 No.12:59
24 years old male, previously healthy, presented with a 6 months history of fever, back pain, left sided upper back swelling and weight loss. US soft tissue of the back showed superficial intramuscular large collection of asymmetric thick wall showing complex content. CT thorax showed right upper loculated pleural collection with enhancing wall extending to the soft tissue of right upper lateral chest wall associated with bony destruction and a left large intramuscular collection involving the left para spinal muscles with mild extension to the right side, and there is a tiny bone fragments in the posterior lower part of the collection communicating with the left paraspinal/prevertebral collection. Fine needle aspiration of the fluid was sent for analysis, was positive for TB AFB Smear and PCR. Patient was started on Anti-TB and referred for thoracic surgeon to be followed in outpatient clinic.
Keywords
Cold abscess; Inflammation; Tuberculosis; Subcutaneous semaglutide
Introduction
Cold abscess refers to an abscess that lacks the intense inflammation usually associated with infection. This may be associated with infections due to bacteria like Tuberculosis [1] and fungi like Blastomycosis [2] that do not tend to stimulate acute inflammation. Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes Tuberculosis (TB) and is a leading infectious cause of death in adults worldwide [3]. Musculoskeletal tuberculosis is relatively uncommon and accounts for about 1 to 2% of all the tuberculosis patients [4,5] and accounts for about 10% of all extra-pulmonary TB infections. Tuberculosis of the chest wall constitutes 1 to 5% of all cases of musculoskeletal TB [6,7]. Cold abscess arising from soft tissue is more uncommon. Here we present a case of a young previously healthy male presenting with constitutional symptoms and left upper back swelling turning out to be tuberculosis.
Case Presentation
24 years old male, presented with 6 months history of fever, back pain and left sided back swelling. The fever was on and off throughout the day and was associated with night sweats. He was also complaining of progressive left sided back swelling, initially was small in size, increasing over the months, was painless but started to be slightly painful over the last few days prior to presentation. No history of trauma. He had no swelling elsewhere. Had significant weight loss of 12 kg over the past 6 months. His father had Pulmonary TB. He works as a scaffolder. He is not smoker, no alcohol use.
On examination, he had fever documented as 38.5, other vitals were unremarkable, his chest examination was clear with good breath sounds bilaterally and normal vesicular breathing. Back Examination revealed a swelling on the left scapular region about 10 × 4 cm, no skin changes, redness or sinus drainage; it was soft, fluctuating with Mild tenderness (Figure 1). There was no other visible or palpable swelling. Remaining of the examination was unremarkable (Figure 2 and Table 1).

Figure 1: Left scapular swelling.

Figure 2: Unremarkable Chest XR.
| Detail |
Value w/units |
Flags |
Normal Range |
| Calcium |
2.20 mmol/L |
NA |
- |
| Adjusted Calcium |
2.34 mmol/L |
NA |
2.20-2.60 |
| Albumin Lvl |
33 gm/L |
Low |
35-50 |
| WBC |
8.9 × 10^3/uL |
NA |
4.0-10.0 |
| RBC |
4.4 × 10^6/uL |
Low |
4.5-5.5 |
| Hgb |
9.6 gm/dL |
Low |
13.0-17.0 |
| Hct |
30.2% |
Low |
40.0-50.0 |
| MCV |
67.9 fL |
Low |
83.0-101.0 |
| MCH |
21.5 pg |
Low |
27.0-32.0 |
| MCHC |
31.7 gm/dL |
NA |
31.5-34.5 |
| RDW-CV |
15.6% |
High |
11.6-14.5 |
| Iron |
2.06 umol/L |
Low |
11.60-31.30 |
| TIBC |
49 umol/L |
NA |
45-80 |
| Transferrin |
1.94 gm/L |
Low |
2.00-3.60 |
| Fe% Saturation |
4% |
Low |
15-45 |
| Ferritin |
193.2 mcg/L |
NA |
24.0-336.0 |
| Vit B12 |
103 pmol/L |
Low |
133-675 |
| Urea |
2.8 mmol/L |
NA |
2.5-7.8 |
| Creatinine |
69 umol/L |
NA |
64-110 |
| Sodium |
133 mmol/L |
NA |
133-146 |
| Potassium |
3.9 mmol/L |
NA |
3.5-5.3 |
| Chloride |
101.4 mmol/L |
NA |
95.0-108.0 |
| Bicarbonate |
25.5 mmol/L |
NA |
22.0-29.0 |
| Bilirubin T |
12.7 umol/L |
NA |
3.4-20.5 |
| Total Protein |
76 gm/L |
NA |
60-80 |
| CRP |
111 mg/L |
High |
0-5 |
| Procalcitonin |
0.15 ng/mL |
NA |
- |
Table 1 Results of lab examination.
US Soft tissue thoracic region of back was done which demonstrated superficial intramuscular large collection of asymmetric thick wall showing complex content (with internal echoes) is noted at the site of complaint in the posterior chest wall left to midline (Figures 3 and 4).

Figure 3: Intramuscular collections showing asymmetric thick wall.

Figure 4: Intramuscular collection.
CT Thorax with contrast was done which demonstrated right upper loculated pleural collection with enhancing wall extending to the soft tissue of right upper lateral chest wall associated with bony destruction anterior part of right second rib measuring 5.8 × 3.6 × 6 cm (CC × AP × W) (Figure 5). There is a large intramuscular collection involving the left para spinal muscles with mild extension to the right side, and there is a tiny bone fragments in the posterior lower part of the collection, the collection measures 14 × 2.2 × 8 cm (CC × AP × W) , it communicate with the left paraspinal/prevertebral collection at the level of T6,measuirng 14 × 2 × 3.4 cm , the paraspinal collection extending from (T4- T9 level) associated with bone destruction of the posterior part of left sixth rib and extending through the left exit neural foramina of T6 abutting the Dural sac (Figure 6). There is no focal parenchymal lesion. Mediastinal vessels are normal. There are multiple mediastinal lymph nodes also measuring 11 mm in the upper right paratracheal region.

Figure 5: CT Thorax of right pleural collection.

Figure 6: Left intramuscular collection.
Fine needle aspiration was done for the back swelling (Figure 7) which revealed thick creamy fluid. The fluid was sent for work up including Tuberculosis Acid Fast Bacilli Smear and PCR which turned as positive for Tuberculosis. Gram stain and culture were negative. The patient was treated as a case of intramuscular tuberculous cold abscess and was started on anti-TB medication along with pyridoxine. Thoracic surgery team was consulted, they opted for medical treatment and will follow in their clinic. The patient was discharged in good condition with appropriate follow up and medications given.

Figure 7: Swelling aspirate.
Discussion
Tuberculosis is a common endemic disease mainly leading to pulmonary disease. Musculoskeletal tuberculosis is relatively uncommon and accounts for 1 to 2% of all the tuberculosis patients [4,5] and accounts for about 10% of all extra pulmonary TB infections. Tuberculosis of the chest wall constitutes 1 to 5% of all cases of musculoskeletal TB [6,7]. In this case, we report a patient with progressive upper back lump, further work up revealed, intramuscular collection with extension to the paraspinal muscle and underlying bone involvement. CT showed another collection arising from the right upper pleura and extending to the right upper soft tissue with underlying bone destruction but no lung involvement. Intramuscular tuberculous cold abscess is a rare presentation of tuberculosis with very few cases reported. One case was reported where a patient developed deltoid muscle cold abscess and was diagnosed with TB due to possible reactivation of BCG vaccine [8]. Another case series reports 5 children developing intramuscular TB after intramuscular injection [9]. Another case reported an 8-year-old child developing multiple muscular swelling, biopsy from these sites demonstrated cases necrosis consistent with TB [10].
Conclusion
Intramuscular cold abscess due to tuberculosis is an uncommon manifestation of tuberculosis and should be considered as a differential diagnosis especially in patient from endemic countries.
42074
References
- Kumar GR, Somvanshi DS (2011) Spinal tuberculosis: A review. J Spinal Cord Med 34: 440-454.
- Fred F. Blastomycosis. Ferri's Clinical Advisor. Philadelphia: Mosby (Elsevier). 198(2015) e2-e4.
- García S, Combalia A, Serra A, Segur JM, Ramon R (1997) Unusual locations of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116: 321-323.
- Dong SC, Rafii M, McGuinness G, Jagirdar JS (1998) Primary multifocal tuberculous osteomyelitis with involvement of the ribs. Skeletal Radiol 27: 641-645.
- Gayler BW, Donner MW (1967) Radiographic changes of the ribs. Am J Med Sci 253: 586-619.
- Mathlouthi A, Ben M'Rad S, Merai S Friaa T (1998) Tuberculosis of the thoracic wall. Presentation of 4 personal cases and review of the literature. Rev Pneumol Clin 54: 182-186.
- Kulkarni AG, Kulkarni SA (1990) Primary intramuscular cold abscess in the left deltoid region: A case report. East Afr Med J 67: 922-923.
- Blankoff B, Richard J, Chevalier V, Delcourt J (1955) Invasion tuberculeuse chez l'enfant par abcès froids consécutifs à des injections intramusculaires; à propos de 5 cas [Tuberculous infection in the child caused by cold abscesses after intramuscular injections; report of five cases]. Acta Paediatr Belg 9: 69-77.
- Kumar DA, Shah SC, Devendra Shrestha, Banepali N (2015) Tuberculosis presenting as multiple intramuscular nodules in a child: A case report. J Med Case Reports 9.