Keywords
|
| In 2007 Dalmau et al. [1] described 12 women with prominent psychiatric symptoms, amnesia, seizures, frequent dyskinesias, autonomic dysfunction, and decreased level of consciousness associated with teratoma and antibodies anti-N-Methyl-DAspartate receptor (NMDAR) [1]. Since then, anti-NMDAR encephalitis has been increasingly recognized not only in adults but also in children. |
| The objective of this study is to report the clinical and EEG findings of a child with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, with emphasis on a recently described EEG finding called extreme delta brush. |
Case Report
|
| This six-year-old boy was admitted at our University Hospital showing agitation, involuntary movements characterized by asymmetric fast movements of high amplitude of arms and legs, more frequent at the right side. He could not recognize his family and was not able to talk. Twenty days prior to his admittance to the hospital, he had two complex focal seizures lasting one or two minutes each. At this time also appeared abnormal movements and behavioral changes that progressively worsened. |
| Neurological examination showed severe somnolence with no eye contact. He had bilateral choreoathetosis, mostly in the right arm and leg. He had normal muscle strength, normal deep tendon reflexes, and normal cranial nerves. Gait and coordination could not be evaluated due to his extreme somnolence. Signs of meningeal irritation were absent. |
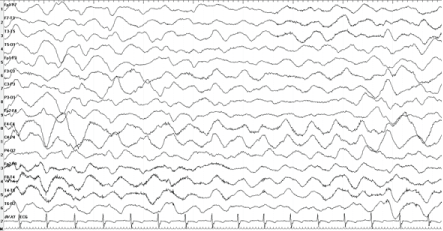
| Brain MRI was normal. Cerebral spinal fluid showed red blood cells=3/mm3, ellcount=5/mm3, glucose=80 mg/dL and protein=16 mg/dL. EEG showed diffuse slowing associated with rhythmic delta activity 1-3 Hz with superimposed bursts of rhythmic 20- 30 Hz beta frequency activity on each delta wave (Figure 1). Antibodies against NMDA receptor were positive in both cerebral spinal fluid and serum. |
| Extensive investigation for tumor was negative. We started valproic acid (40 mg/kg/day) for seizure, risperidone (2 mg/day) for extrapyramidal and behavior symptoms, and clonazepam 0.1 mg/kg/day for all symptoms. Seizures and choreoathetosis were easily controlled, but not the agitation. |
| He was treated with intravenous gammaglobulin (400 mg/ kg/day for 5 days) followed by prednisolone (30 mg/kg/day for 5 days) with poor improvement. One cycle of 500 mg/m2 of cyclophosphamide was administered. One week after the beginning of this treatment, he started to show slow behavior improvement. |
| After two months, the aggressive behavior and severe agitation persisted. A second cycle of IVIg (400 mg/kg/day for 5 days) followed by a second cycle of cyclophosphamide was administered, following prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day for 3 months. Risperidone was increased to 4 mg/day and clonazepam to 0.18 mg/kg/day. |
| Six months after the first symptom prednisolone and clonazepam were tapered off. Since then, his symptoms improved dramatically. |
| He was able to go back to school and neurological examination was normal. |
| After 18 months he remains with normal neurological examination and behavior. All medications were tapered off. The only complaint is poor school performance. Neuropsychological examination to address cognitive impairment was not performed. |
Discussion
|
| Anti-NMDAR encephalitis is probably the most common paraneoplastic encephalitis [2]. Since the description of anti- NMDAR encephalitis in adults, it has been increasingly recognized in children, comprising 40% of all cases. Children often do not have tumors; and dysautonomia and hypoventilation are also less frequent than in adults. Seizures, behavioral and abnormal movements are the most frequent symptoms [3]. |
| The diagnosis is confirmed by the demonstration of the antibody anti-NMDAR. Cognitive deficits constitute a major long-term morbidity of anti-NMDAR encephalitis [4]. |
| Electroencephalogram (EEG) is abnormal in most patients, usually showing non-specific slowing. Epileptiform abnormalities might be present sometimes with electrographic seizures [5]. Slow, rhythmic delta activity predominates in the catatonic-like stage. This activity is not associated with abnormal movements and does not respond to antiepileptic drugs [3,6]. |
| Recently, a new EEG feature was described in 30% of adult patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis. The authors described a rhythmic delta activity 1-3 Hz with superimposed bursts of rhythmic 20–30 Hz beta frequency activity “riding” on each delta wave. The name extreme delta brush applies because of its resemblance to the waveforms seen in premature babies [7]. |
| The most distinctive EEG pattern in the acute phase of anti- NMDAR encephalitis is probably a non-ictal rhythmic delta or theta slow activity independent of movements or clinical status. It is also unresponsive to medications [8]. |
| Extreme delta brush is a pattern that can be observed in some of the patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, but it is not a constant feature. Its presence appear to be associated with a more prolonged illness, although the specificity of this pattern is unclear [9]. |
| Extreme delta brushes in childhood were described in only a few studies [6,10,11]. In one pediatric series, the frequency of this EEG pattern was only 5% [10]. It remains unclear if the systematic evaluation of continuous EEG of children with anti- NMDAR encephalitis would show a frequency similar to the one found in adults. |
| Although the specificity of this pattern is unclear, its identification may guide to an early diagnosis and treatment of anti-NMDAR encephalitis [7,12,13]. This is extremely important, because good long-term cognitive outcome may depend on early and ag gressive treatment [4]. |
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
|
| The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. |
Author Contribution
|
| All authors participated in the patient care and manuscript preparation. |
Funding
|
| Supported by FAPESP. |
Ethical Approval
|
| This study was done in accordance with the rules set by the University of Campinas institutional review board. |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
| Figure 1 |
|
| |