Introduction
Hospital is made of subsystem different clinical department; nursing department support service, diagnostic service, auxillary services. The best way of service is matrix organization. The hospital is made of series of departments which work together in rendering, medical, nursing service, support service. Hospital as an organization within larger spectrum of health care, hospital as complex organization having departments of multi-discipline managed by medical, nursing, paramedical and service personnel.
Private hospitals and corporate hospitals are providing medical care services.
Even there is no uniformity between all government hospitals; hence you would see that there is no universal model that can be applied in organizing hospital.
The hospital organizations of this millennium would also be affected by new techniques of medicine, information technology and TQM (Total Quality Management).
The developing countries also must think of health care at affordable cost and thus organize. Organizing is a process of grouping the necessary responsibilities and activities into workable units allying of authorities, communication and developing pattern of coordination would involve systemizing of technical and administrative activities to effect satisfying customers, employers and agencies that make it possible to organize.
The organizational structure would depend on size of hospital.
The hospital is organized under governing body and functions under a hospital administrator. Hospital has broadly five main components:
1. Clinical services where all clinicians under various departments provide medical care to the patients.
2. Nursing services where all nursing personnel provide nursing care to patients.
3. Professional or diagnostic services like laboratory and radiology services.
4. Ancillary services like laundry, dietary and housekeeping services.
5. Auxiliary services like public relation department, welfare service, religious services and hospital inn etc.
The students should study hospital working under these five main components and categories, various department under this subsystem.
The professional service departments are those departments which assist physician and medical team in diagnosing and treating the patient like Laboratory services radiology department, Physiotherapy department and Laboratory services which invariable exist in every hospital hence students should study in detail and visit these departments in hospitals to have better understanding.
According to directory of hospitals, The Directory of Hospitals in India of 1988 lists the various types of hospitals and the types of management [1].
General hospital: All establishments permanently staffed by at least two or more medical officers, can offer to in-patient and provide active medical service, and nursing care which can be offer to in-patient and provide active medical and nursing care for more than one category of different discipline (e.g, general medicine, general surgery, obstetrics, paediatrics etc.).
Rural hospital: Hospitals located in rural areas (classified by the Registrar General of India) permanently staffed by at least one or more physicians, which offer in-patient accommodation and provide medical and nursing care for more than one category of medical discipline (e.g. general medicine, general surgery, obstetrics and paediatrics).
The hospital system has its external environment and linkages. Therefore, to understand the hospital system, one has to look at the hospital as an open system.
The delivery of Primary Health Care is the foundation of rural health care system and forms an integral part of the national health care system.
The program of establishing Primary Health Centres in each Community Development Block having a population of 60,000 to 80,000 was launched as an integral part of the Community development program on October 2, 1952.
Each Primary Health Centre Complex is consisted of the main centre with 6 beds located at the Block Head Quarters, 4 sub centres. The staff consists of 1 Medical Officer, 1 Sanitary- Inspector, 4 Midwives (ANMs) and 2 Ancillary personnel.
The Centre was to be supported by district organization for referral, consultation, Laboratory, medical, surgical, nursing and Administrative personnel.
Rural health care system in India
Community Health Centre (CHC) is a 30 bed Hospital or a referral Unit for four (4) PHCs with Specialized services.
Primary Health Centre (PHC) is a referral Unit for 6 Sub Centres 4-6 bed manned with a Medical Officer – In – charge and 14 subordinate paramedical staff.
Sub Centre Most peripheral contact point between Primary Health Care System & Community manned with one HW (F)/ANM and one HW(M).
Strengthening of rural health infrastructure under national rural health mission
National Rural Health Mission (2005-12) seeks to provide effective healthcare to rural population throughout the country with special focus on 18 states, which have weak public health indicators and/or weak infrastructure [2]. These 18 States are Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Jammu & Kashmir, Manipur, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Madhya Pradesh, Nagaland, Orissa,Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tripura, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh. The Mission is an articulation of the commitment of the Government to rise public spending on Health from 0.9% of GDP to 2% to 3% of GDP.
NRHM aims to undertake architectural correction of the health system to enable it to effectively handle increased allocations as promised under the National Common Minimum Programme and promote policies that strengthen public health management and service delivery in the country. It has as its key components provision of a female health activist in each village; a village health plan is prepared through a local team headed by the Health and Sanitation Committee of the Panchayat; strengthening of the rural hospital for effective curative care and is made measurable and accountable to the community through Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS); integration of vertical Health & Family Welfare Programmes, optimal utilization of funds & infrastructure, and strengthening delivery of primary healthcare. It seeks to revitalize local health traditions and mainstreaming AYUSH manpower.
Functions of the hospital
Though there are many functions of a hospital, all of them are subordinate to its main objectives and must never be allowed to detract in any respect from the care given to sick and injured [3].
1. To provide care for sick and injured.
2. Training of physicians, nurse, and other personnel.
3. Prevention of disease and promotion of health.
Management Development Programme on Health and Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS) will strengthen capabilities of participants on understanding better usage, designing and implementing HMIS.
Dorland’s illustrated Medical Dictionary defines a Hospital as an institution suitably located, constructed, organized staffed to supply scientifically, economically, efficiently and unhindered all or any recognized part of the complex requirement for prevention, diagnosis and treatment of physical, mental and medical aspect of social ills with functioning facilities for training new workers in many special professional, technical, economical fields, essential to the discharge of its proper functions and with adequate contracts with physicians of other hospitals, medical schools and all accredited health agencies engaged in better health program.
Basic minimum requirements for a hospital of 30 Beds
Functions
Medical and allied disciplines: Anesthesiology, Blood bank, Emergency Medicine, General medicine, General surgery, Obstetrics and gynecology and Pediatrics.
Health and allied services: Family welfare, Health education, Maternal and child health care, Nutrition, School health care.
Nursing, Paramedical and allied services: Dental technology including Dental hygiene, Dietetics, Drugs and pharmacy.
The organization process should culminate into a common goal towards which collective efforts are directed and the goal is spelt out in detail.
There is a need for clear authority responsibility relationship that power and authority factor need to be reconciled so that individual organizations are productive and goal directed and there is clarity of organizational relationship, to reduce conflict that the unity commands and that authority must be delegated.
Research Methodology
Steps in conducting the research
After a defined problem, made a hypothesis to work on, designed the tool a research will start.
1. Data collection.
2. Analysis and interpretation of data.
3. Verification and proving the hypothesis which defined earlier.
4. Writing the report.
5. Making recommendation which can be used practically.
Data collection
Data is the raw, unprocessed details which were collected during the course of study. The data collecting tools and techniques are: Survey, Interviewing, Questionnaire and Observations.
Analysis and interpretation of data
After the raw material is collected, it is to put in a systematic form e.g. tables, bar diagrams etc.
Now in this systematic form it becomes easy to analyze details and interpret the data. This becomes “information" for the researcher which he/she can document and use in drawing conclusions and making recommendations.
Once you have interpreted the data, the next step is to discuss the results. It should highlight two aspects:
Bring out the implications of the data.
The findings are entirely new and have not been thought of to be frequent. Fortunate indeed is the author whose work comes into this category.
Primary data
Data is collected through observation methods of rural hospital staffs to know about staffs patterns, to know actual figure of staffs’ strength. Some staffs are interviewed through face to face conversation which help to know staffs hierarchy of this institute and their area of works, by whom their works are evaluated, Questionnaires methods will helpful to collect primary data.
Sampling
Judgement sampling is called purposive sampling; this sampling procedure will help to collect sample from representative of the population, case study method will help to understand total system what are co-relation of different staffs is with each other, By interviewing in-patient and outpatient actual condition rural hospital will come out.
To study this topic out patients and different levels staffs there are 250 staffs to run this hospital,5% staffs are selected as sample among 1500 patient s 2% are interviewed this sample are collected through simple random sampling. this study is done at Salboni Block, Paschim Medinipur.
Monthly report of every department helps to find ratio patient and facility provider, and what feedback from patient is to study this topic out patients and different levels staffs there are 250 staffs to run this hospital, 5% staffs are selected as sample among 1500 patient s 2% are interviewed this sample are collected through simple random sampling. This study is done at Salboni Block, Paschim Medinipur (Tables 1 and 2).
| Outdoor Service |
Good |
Excellent |
Average |
Not up to the Mark |
| Specialist doctor |
50 |
43 |
20 |
10 |
| Pharmacy |
40 |
24 |
45 |
20 |
| Dental service |
32 |
20 |
35 |
23 |
| dressing |
25 |
10 |
15 |
28 |
Table 1: Outdoor service quality of different department.
| |
Grading of service |
| Different Service |
Bad |
Good |
Excellent |
Average |
| Vaccination |
20 |
45 |
65 |
34 |
| Antenatal Care |
10 |
75 |
30 |
20 |
| Laboratory Facility |
9 |
85 |
20 |
23 |
| Radiology |
15 |
37 |
23 |
34 |
| ECG |
4 |
43 |
47 |
58 |
| Ambulence |
2 |
43 |
45 |
64 |
| Counselling Service |
5 |
45 |
53 |
20 |
| Sterilization |
2 |
30 |
34 |
45 |
Table 2: Different facility available for rural hospital.
Monthly report of every department helps to find ratio patient and facility provider and feedback from patient. Performance appraisal processes help to get data because it establishes standard performance, communicating performance standard of employees (Graphs 1 and 2).
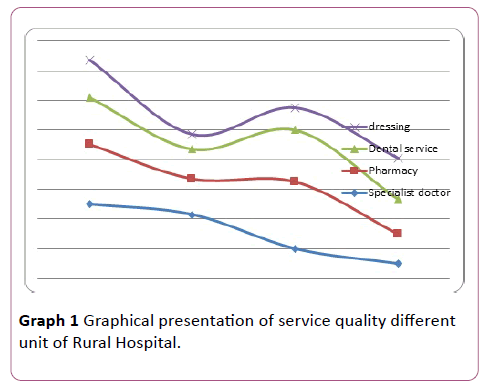
Figure 1: Graphical presentation of service quality different unit of Rural Hospital.
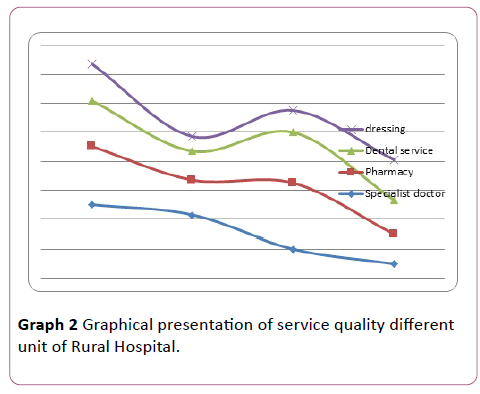
Graph 2: Graphical presentation of service quality different unit of Rural Hospital.
Analysis
After data collection, this study indicates that 65 persons are very much satisfied in child Vaccination about 75 persons are satisfied with antenatal care which is mostly delivered through sub-centre, but for delivery purpose only normal delivery is organised due lack of equipment no facility for caesarean, those cases are referred to nearest Midnapur Medical College & Hospital, BPL/SC/ST mother get benefit Jannani Surakhsa yojana for Ambulances service and Mother nutrition Supplement. Sister attitude is not well but Sub centre ANM are best in their service. Counselling service are very useful for adolescent’s problem and problem of Sexually transmitted infection (STI), Family Planning, HIV-AIDS service. In point of view contractual staffs are not satisfied for low pay scale, seniors, attitude, they are deprived from facility of Government.
Literature Review
The hospital administrator basically works at the background to make hospital service up to the level. They ensure that the hospital runs effectively and efficiently.
At this point you must not go away with the impression as there is only one person as the hospital administrator managing the entire Hospital all alone.
In Salboni there are routine immunization, outreach facility which are running by Salboni Rural hospital fieldworkers, ANM(R) (Auxiliary nursing and midwifery) staffs their works are supervised by Health Supervisor, supervisor is evaluated by BPHN (Block Public Health Nurse), those kinds of staffs deliver health services rural people of salboni block through Subcenter which are situated in ten-gram panchayat of block with association of local Government receive medical service.
Personnel management is concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, orientation, salary administration performance appraisal, training, working conditions, safety, welfare, promotion, transfer, collective bargaining.
Primary health care is defined as essential health care, which is based on practical scientifically sound, socially acceptable methods, and technology, made universally accessible to people.
This essentially means a holistic approach, which is low cost and appropriate to local people and conditions.
The health facilities will be fully utilized and equipped to implement national programme.
Each district: A District health centre with specialized curative services and public health experts.
Each subdivision: (Approximately 5 lakh population). A subdivisional health centre with epidemiological wing attached to it.
Each block: (One lakh population) community health centre having specialists offering medical care services in gynaecology, Paediatrics, surgery, medicine. There are four non-specialist doctors. (General duty)
Community health center will have 30 beds. It serves as a referral centre for four PHCs.
For 30,000 population (or 15,000-20,000 in case of hilly, tribal sparsely populated or desert areas). Primary health system is the first contact point between village community and the medical officer.
A PHC is manned by medical officer supported by 15 para medical staffs. It acts as a referral unit of six sub-centres. It has 4-6 beds. A PHC will be fully equipped to render preventive, promotive and curative services. Primary health care is defined as essential health care, which is based on practical scientifically sound, socially acceptable methods and technology, made universally accessible to people.
This essentially means a holistic approach, which is low cost and appropriate to local people and conditions.
The Alma Ata Declaration states that there primary health care should at least have the Following components
i) Education of people regarding prevailing health problems and methods of preventing and controlling the same.
ii) Promotion of food supply and proper nutrition.
iii) Adequate supply of' safe water and basic sanitation.
iv) Maternal and child health and family planning.
v) Immunization against major infectious diseases.
vi) Prevention and control of locally endemic diseases.
Existing rural dispensaries will be upgraded with additional funds, equipment and expansion of staff building.
Staff for New primary Health centre.
Medical officer.
Pharmacist.
Nurse midwife.
Female Health worker (AWM).
Health educator.
Male health Assistant.
Female Health assistant.
Upper Division Clerk.
Lower division Clerk.
Lab technician.
Driver.
Class IV.
For 5,000 population (or 3,000 population in the case of hilly, tribal, sparsely populated or desert areas) Sub-centre is the most peripheral contact point between the primary health care system and community.
One sub-centre will have one MPW (Female), MPW (Male) and one part time attendant. It will provide antenatal, natal, and post-natal care for pregnant women. For each village with 1000 population (or 500 population in case of hilly and tribal areas or sparsely populated or desert areas). A village health guide was appointed for population of 1000 peoples. She was trained for a period of three months and was equipped with manual of instruction and a medicine kit.
Period of three months was equipped with manual of instruction and a medicine kit. A stipend of Rs/- 2001 was given during training and thereafter a stipend of Rs 50/- per month was given. It was started as a 100 per cent centrally sponsored program in 1977 but in 1979, states given. Subcentre is the most peripheral contact point between the primary health care system and community. One sub-centre, will have one MPW (Female), MPW (Male) and one part time attendant. It will provide antenatal, natal and post-natal care for pregnant women.
For each village with 1000 population (or 500 population in tlie case of hilly and tribal areas or sparsely populated or desert areas). A decentralized, participatory approach involving the community intimately in the planning, implementation and maintaining the health services was recommended.
A village health guide was appointed for population of 1000 peoples. She was trained for a period of three months and was equipped with manual of instruction and a medicine kit.
Block Level
Rural areas of the district have been organized into blocks, known as Community Development Blocks. The block is a unit of moral planning and development and comprises approximately 100 villages and about 80,000 to 1,20,000 population.
To provide effective services and referral support to primary health care programme, one Community Health Centre (CHC) is being established in each programme.
One Community Health Centre (CHC) is being established in each block.
The CHCs are framed by upgrading some of the block level PHCs or by creating new centres, whenever absolutely needed.
The officer in-charge f CHC is known as superintendent CHC or medical officer in-charge block PHC.
Each CHC has been envisaged to get primary and secondary care and of one lakh population. It is intended to be a first level referral institution. Normally one CHC should have 4 Medical Officers who are either qualified or specially trained to work. as Surgeon, Obstetrician, Physician and Paediatrician. It is intended to be a first level referral institution.
According rural health system of West Bengal
BMOH (Block Medical officer of Health)Medical officers---- BPHN----Health Supervisor----ANM(Auxiliary Nursing Midwifery(R)(Sub centre)---ASHA(Accredited Social Health Activist(over 1000 Population)---Link Persons.
BMOH- Sister-in charge-Staff Nurse-Gr-D staffs-Sweepers.
BMOH---Medical Officers (Primary Health Centre, Rural Hospital)-Pharmacists & Medical Lab technicians-- Administration.
At time of NRHM BMOH-Head Clerks-Upper divisional clerk- Lower division Clerk in Office.
BMOH acts as Member secretary.
Member Secretary-Block Accounts Manager—Data entry operators.
According guidelines NRHM for Rogi kalyan Samiti: Rogi Kalyan Samiti (Patient Welfare Committee)/ Hospital Management Society is a simple yet effective management structure. This committee, which would be a registered society, acts as a group of trustees for the hospitals to manage the affairs of the hospital. It consists of members from local Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs), NGOs, local elected representatives and officials from Government sector who are responsible for proper functioning and management of the hospital/Community Health Centre/FRUs. RKS/HMS is free to prescribe, generate and use the funds with it as per its best judgments for smooth functioning and maintaining the quality of services.
A Chief Medical Officer of Health (C.M.O.H.) heads each of the eighteen districts. The responsibility of CMOH is to manage the primary health care sector and ensure the effective implementation of the various medical, health and family welfare programmes. The secondary level hospitals (subdivisional and district hospitals) are headed by superintendents who report to the C.M.O.H. and are accountable to a hospital management committee. At the block level, the Block Medical Officer of Health (BMOH) is responsible for providing services and for monitoring and supervising the primary health centres and health programme implementation [4-7].
There is new scheme launched like Paras nutrition rehabilitation centre to supplement nutrition to carrying mothers, underweight children, Ayush to provide homeopathic treatment to rural people and school health programme in which 1 Gnm Nurse, a homeopathy and ayurvedic doctor ASHA (accredited social health activist) act as mediator to health service and local public.
Conclusion and Contributions
It will be helpful for future staff strengthening,
It will help to evaluate staff performance.
Management control system will be helpful to find out draw back in staff hierarchy.
Limitations
At time of interview, if staffs delivered false information, it may hamper study.
At time of interview, the patient may act as an ill informant.
18283
References
- Directory of Hospitals in india(1998) Central Bureau of Health Intelligence,Ministry of Health and Family welfare,New Delhi.
- Sharma DK,Goyal RC (2010) Hospital Administration, Hospital Administration and Human Resource Management(5thedn) PHI learning private limited, New Delhi Eastern India publication 95-43.
- SubhaRKB (2011)Planning a modern Hospital: Managing Modern Hospital (2ndedn )By A.V. Srivasan(ed)by Response Business Books from Sage Publications,Sixth Printing, Los Angles.
- World Health Organization (1978) Declaration of Alma ata adopted at the internet conference on primary Health care.Alma-Ata,USSR 6-12.
- World Health Organization (1978) Decleration of Alma ata adopted at the internet conference on primary Health care,Alma-Ata,6th-12thseptember,USSR.
- Chandrashekar SF(1998)Hospital organization structure-book chapter of Managing Modern Hospital (2ndedn) A.V Srinivas(ed) Sage Publications,USA.
- Directory of Hospitals in India(1988) Central Bureau of Health Intelligence,Ministry of Health and Family welfare,New Delhi.