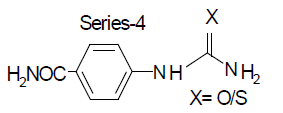Introduction
The structure activity relationship study for the synthesised eight compounds has been divided into two series: 2-substituted and 4-substituted phenyl ureas having variable atoms in (X). X=O (urea) and X=S (thiourea) for carboxylic acid and carboxamide substitutions in phenyl ring produces open chain ureas which have been screened for CNS depression study by using closed chain ureas (barbiturate=pentobarbitone) and bioisosteric closed chain ureas (benzodiazepines=diazepam) to identify the correlation analogy between closed chain and open chain ureas on CNS depression and sleeping time potentiation[1-3].
Series of Synthesized Molecules:-
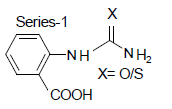
Compound-1: 2-carboxy-phenyl urea
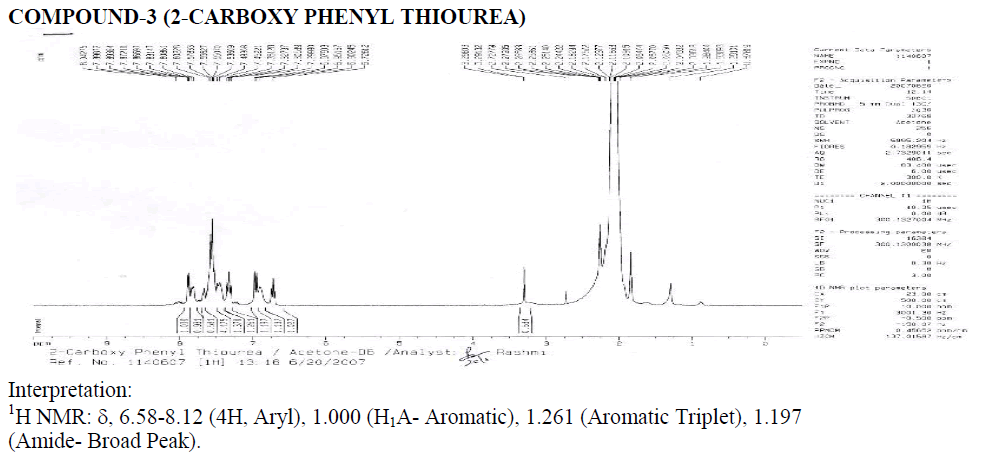
Compound-3: 2-carboxy-phenyl thiourea
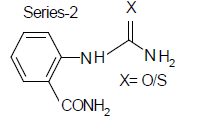
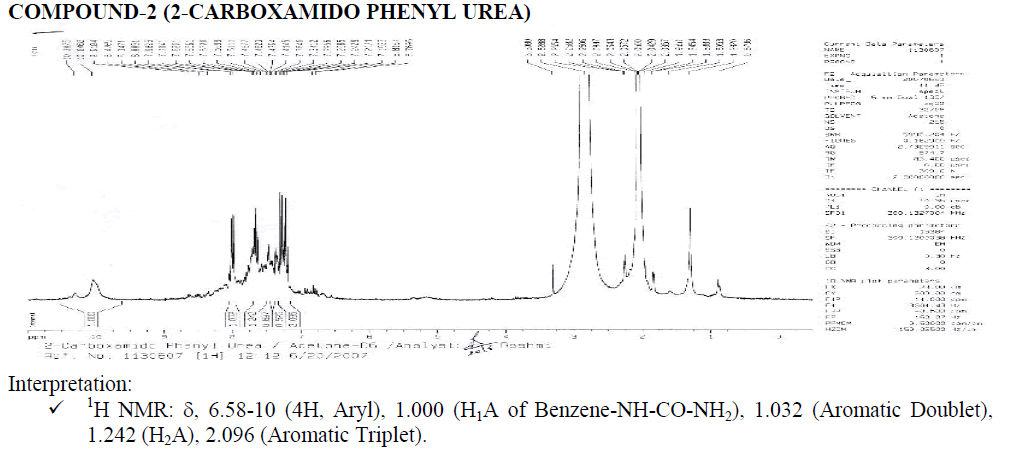
Compound-2: 2-carboxamido-phenyl urea
Compound-4: 2-carboxamido-phenyl thiourea
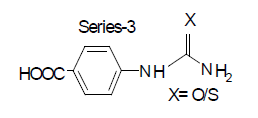
Compound-5: 4-carboxy phenyl urea
Compound-7: 4-carboxy phenyl thiourea
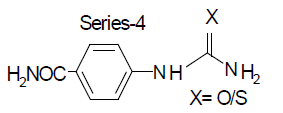
Compound-6: 4-amido phenyl urea
Compound-8: 4-amido phenyl thiourea
Scheme for Synthesis of Compounds (1-4):-
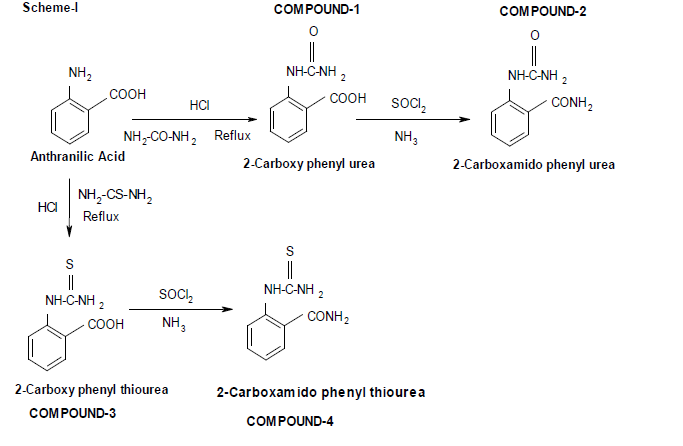
Synthesis[4-8]:
Synthesis of 2-carboxy phenyl urea:
Compound-1:
Anthranilic acid (mol) was first treated with hydrochloric acid to make its hydrochloride salt. Then it was refluxed with urea (mol) for one hour until all the solids has been solubilised. The solubilised mass was cooled in ice to get the solid. It was filtered and recrystallized from benzene-ethanol mixture to get pure product: Compound-1.
Synthesis of 2-carboxamido phenyl urea:
Compound-2:
2-carboxy phenyl urea (mol) was refluxed with thionyl chloride (mol) for one hour until the entire solid has been dissolved. It was cooled and treated with strong ammonium hydroxide to get the solid[7]. It was then recrystallized with aqueous ethanol to get the pure product: Compound-2.
Synthesis of 2-carboxy phenyl thiourea:
Compound-3:
Anthranilic acid (mol) was first treated with hydrochloric acid to make its hydrochloride salt. Then it was refluxed with thiourea (mol) for one hour until all the solids has been solubilised. The solubilised mass was cooled in ice to get the solid. It was filtered and recrystallized from benzene-ethanol mixture to get pure product: Compound-3.
Synthesis of 2-carboxamido phenyl thiourea:
Compound-4:
2-carboxy phenyl thiourea (mol) was refluxed with thionyl chloride (mol) for one hour until the entire solid has been dissolved. It was cooled and treated with strong ammonium hydroxide to get the solid. It was then recrystallized with aqueous ethanol to get the pure product: Compound-4.
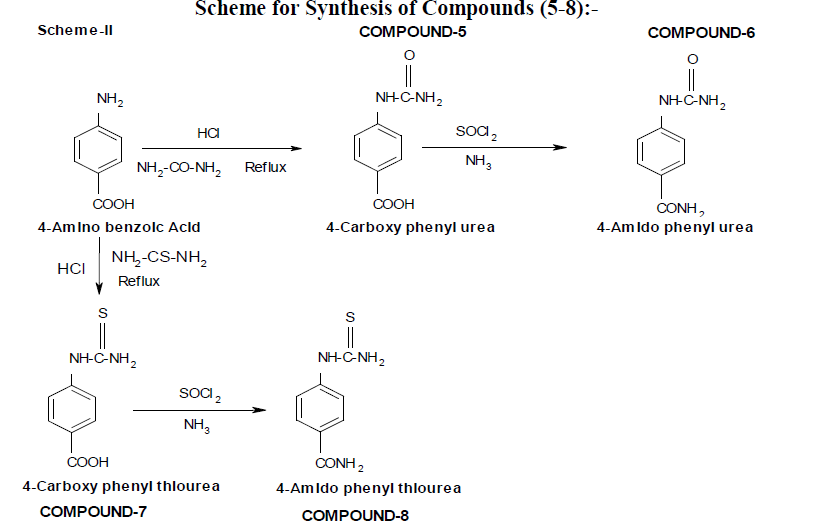
Synthesis[9-12]:
Synthesis of 4-carboxy phenyl urea:
Compound-5:
4-amino benzoic acid (mol) was first treated with hydrochloric acid to make its hydrochloride salt. Then it was refluxed with urea (mol) for one hour until all the solids has been solubilised. The solubilised mass was cooled in ice to get the solid. It was filtered and recrystallized from benzene-ethanol mixture to get pure product: Compound-5.
Synthesis of 4-amido phenyl urea:
Compound-6:
4-carboxy phenyl urea (mol) was refluxed with thionyl chloride (mol) for one hour until the entire solid has been dissolved. It was cooled and treated with strong ammonium hydroxide to get the solid. It was then recrystallized with aqueous ethanol to get the pure product: Compound-6.
Solubility Parameters:-
Synthesis of 4-carboxy phenyl thiourea:
Compound-7:
Anthranilic acid (mol) was first treated with hydrochloric acid to make its hydrochloride salt. Then it was refluxed with thiourea (mol) for one hour until all the solids has been solubilised. The solubilised mass was cooled in ice to get the solid. It was filtered and recrystallized from benzene-ethanol mixture to get pure product: Compound-7.
Synthesis of 4-amido phenyl thiourea:
Compound-8:
4-carboxy phenyl thiourea (mol) was refluxed with thionyl chloride (mol) for one hour until the entire solid has been dissolved. It was cooled and treated with strong ammonium hydroxide to get the solid. It was then recrystallized with aqueous ethanol to get the pure product: Compound-8.
Solubility Parameters:-
| Compounds |
Solubility |
Polarity |
| 2-CARBOXY PHENYL UREA |
Hot Water (1mg/ml), Methanol (2mg/ml) |
Semi polar |
| 2-CARBOXAMIDO PHENYL UREA |
Hot Water (1mg/ml) |
Semi polar |
| 2-CARBOXY PHENYL THIOUREA |
Water (1mg/ml), Methanol (1mg/ml) |
Polar |
| 2-CARBOXAMIDO PHENYL THIOUREA |
Hot Water (1mg/ml) |
Semi polar |
| 4-CARBOXY PHENYL UREA |
Water (1mg/ml), Methanol (2mg/ml) |
Polar |
| 4-AMIDO PHENYL UREA |
Hot Water (1mg/ml) |
Semi polar |
| 4-CARBOXY PHENYL THIOUREA |
Water (1mg/ml), Methanol |
Polar |
| 4-AMIDO PHENYL THIOUREA |
Hot Water (1mg/ml) |
Semi polar |
Table-1
Physicochemical Parameters:-
| Compounds |
%
Yield |
M.P.
ºC |
Polarity |
Molecular
Formula |
N%
Calculated |
N%
Found |
| 2-CARBOXY PHENYL UREA |
77.37% |
158-
162 |
Semi
Polar |
C8H8N2O3 |
15.555 |
15.983 |
| 2-CARBOXAMIDO PHENYL UREA |
68.33% |
101-
103 |
Semi
Polar |
C8H9N2O2 |
16.969 |
17.218 |
| 2-CARBOXY PHENYL THIOUREA |
82.48% |
176-
178 |
Polar |
C8H8N2O2S |
14.285 |
14.574 |
2-CARBOXAMIDO PHENYL
THIOUREA |
56.66% |
120-
122 |
Semi
Polar |
C8H9N2OS |
15.469 |
15.872 |
| 4-CARBOXY PHENYL UREA |
80.29% |
260-
262 |
Polar |
C8H8N2O3 |
15.555 |
15.886 |
| 4-AMIDO PHENYL UREA |
48.33% |
304-
306 |
Semi
Polar |
C8H9N2O2 |
16.969 |
17.438 |
| 4-CARBOXY PHENYL THIOUREA |
76.64% |
252-
254 |
Polar |
C8H8N2O2S |
14.285 |
14.674 |
| 4-AMIDO PHENYL THIOUREA |
71.66% |
295-
297 |
Semi
Polar |
C8H9N2OS |
15.469 |
15.787 |
Table-2
Spectral Datas:-
U.V. Spectras
| Compounds |
lmax |
Absorbance |
| 2-CARBOXY PHENYL UREA |
306.2 |
0.766 |
| 2-CARBOXAMIDO PHENYL UREA |
310.4 |
0.960 |
| 2-CARBOXY PHENYL THIOUREA |
326.8 |
0.939 |
| 2-CARBOXAMIDO PHENYL THIOUREA |
306.6 |
0.314 |
| 4-CARBOXY PHENYL UREA |
277.6 |
0.963 |
| 4-AMIDO PHENYL UREA |
266.6 |
1.940 |
| 4-CARBOXY PHENYL THIOUREA |
279.6 |
0.815 |
| 4-AMIDO PHENYL THIOUREA |
266.4 |
1.294 |
Table-3
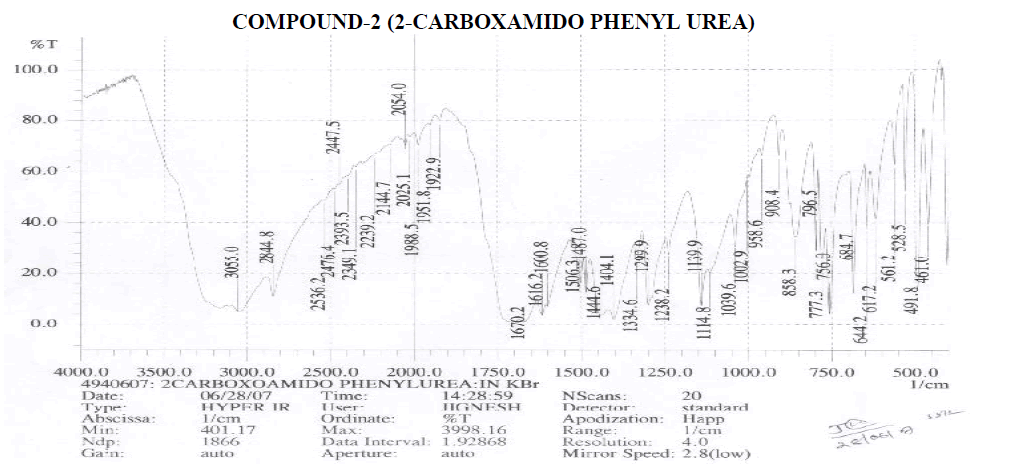
Aromatic
? 3053 cm-1 - Aromatic C-H Stretching.
? 1404.1, 1487 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 684.7, 756, 773.3, 769.5, 858.3 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending.
? 756 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 684.7 (One Band) and 756, 773.3, 796.5 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 796.5 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 1616.2 cm-1 – N-H Bending at Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1037.6 1114.8 1139.9 1238.2 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1404 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
? 1703 cm-1 – C=O Stretching.
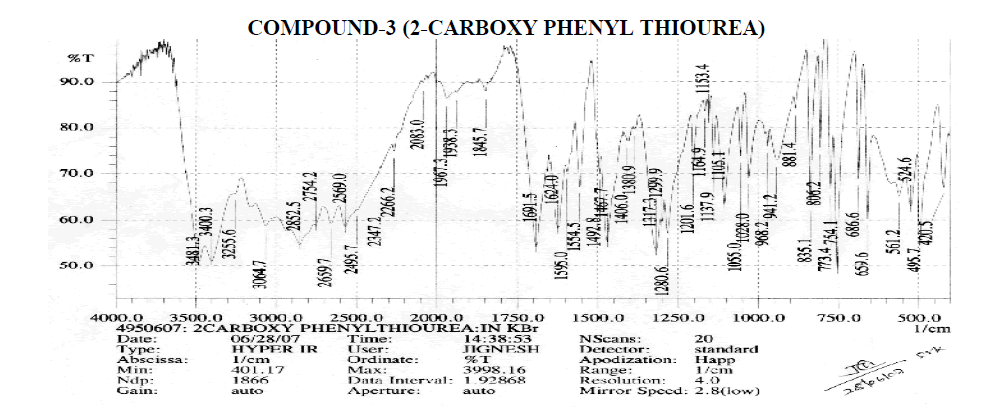
Aromatic
? 3055 cm-1 - Aromatic C-H Stretching.
? 1404.1, 1444.6 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 684.7, 756, 777.3, 796.5, 858.3 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 756 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 684.7 (One Band) and 756, 777.3, 796.5 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 796.5 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2239.2 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching.
? 1600.8, 1616.3 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1039.6, 1114.8, 1139.9, 1238.2 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine. Carboxylic Acid
? 1404.1 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
Aromatic
? 3064.7 cm-1 - Aromatic C-H Stretching.
? 1406, 1467.7, 1492.8 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 656.6, 754.1, 773.4, 806.2, 835.1, 881.4 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 754.1 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 686.6 (One Band) and 754.1, 773.4, 806.2 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 806.2, 835.1 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2239.2 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching.
? 3255.6, 3400.3, 3481.3 cm-1 – O-H Stretching.
? 3400.3, 3481.3 cm-1 – N-H Stretching.
? 1595, 1624 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1028, 1055, 1105.1, 1153.4, 1164.9, 1201.6 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1406 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
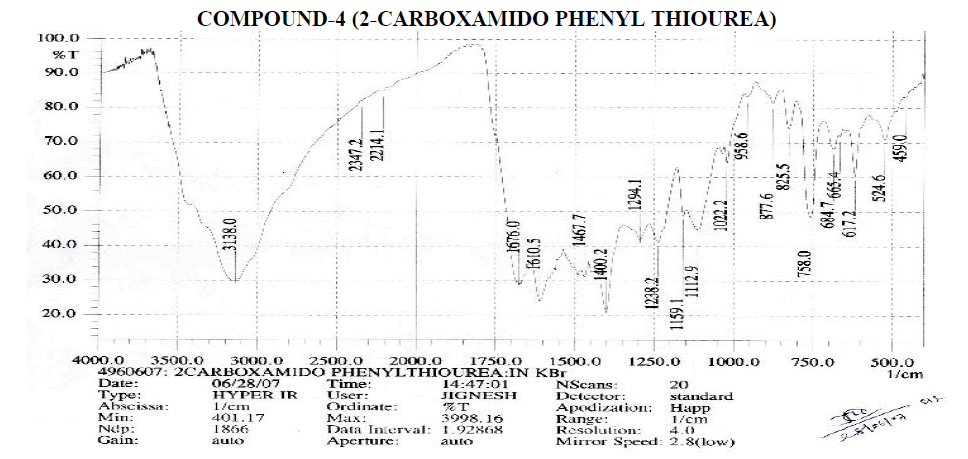
Aromatic
? 1400.2, 1467.7 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 684.7, 758, 825.5, 877.6 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 758 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 684.7 (One Band) and 758 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 825.5 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2214.1 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching
? 1610.5 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1022.2, 1112.9, 1159.1, 1238.2, 1249.1 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1400.2 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
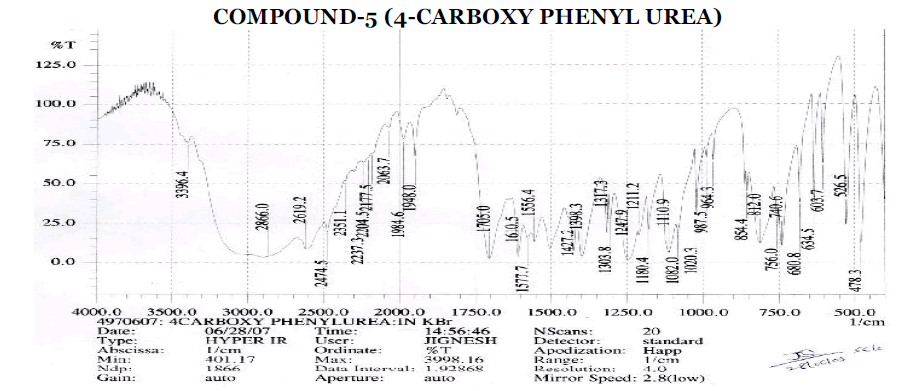
Aromatic
? 1427.2 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 680.8, 740.6, 756, 812, 854.4 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 740.6, 756 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 680.8 (One Band) and 756 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 812 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2237.3 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching.
? 3396.4 cm-1 – O-H Stretching.
? 3396.4 cm-1 – N-H Stretching.
? 1610.5 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1020.3, 1082, 1110.9, 1180.4, 1211.2, 1247.9 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1398.3, 1427.2 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
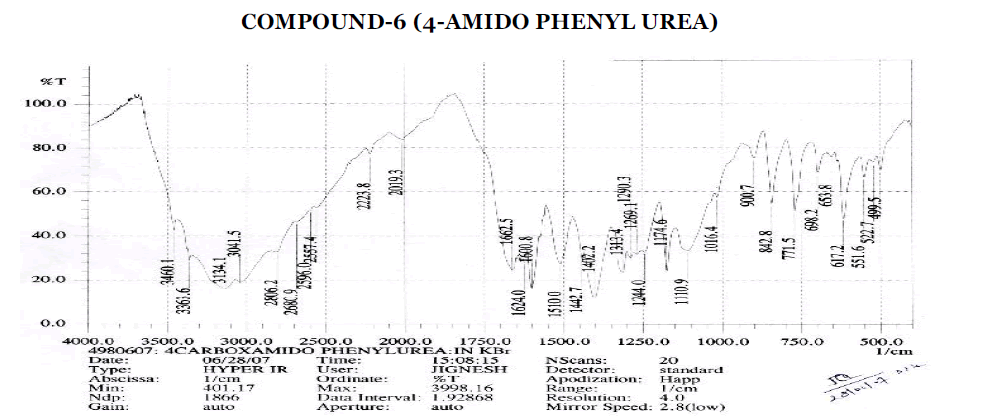
Aromatic
? 3041.5 cm-1 - Aromatic C-H Stretching.
? 1402.2, 1442.7, 1600.8 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 698.2, 771.5, 842.8, 900.7 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 770 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 698.2 (One Band) and 771.5 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 806.2, 835.1 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2223.8 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching.
? 3363.6, 3460.1 cm-1 – O-H Stretching.
? 3363.6, 3460.1 cm-1 – N-H Stretching.
? 1600.8, 1624 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1110.9, 1174.6, 1244 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1402.2, 1440 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
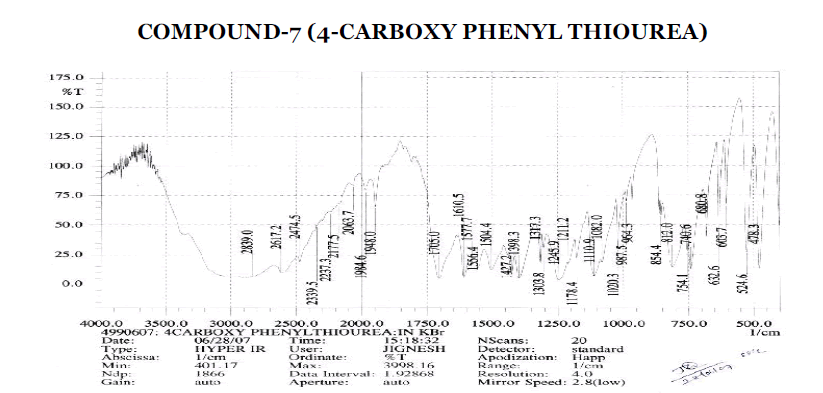
Aromatic
? 1427.2, 1504.4 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 680.8, 740.6, 754.1, 812, 854.4 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 740.6, 754.1 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 680.8 (One Band) and 754.1 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 812, 854.4 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2237.3 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching.
? 3400.3, 3481.3 cm-1 – N-H Stretching.
? 1578.8, 1610.5 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1020.3, 1082, 1110.9, 1178.4, 1211.2, 1245.9 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1398.3, 1427.2 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
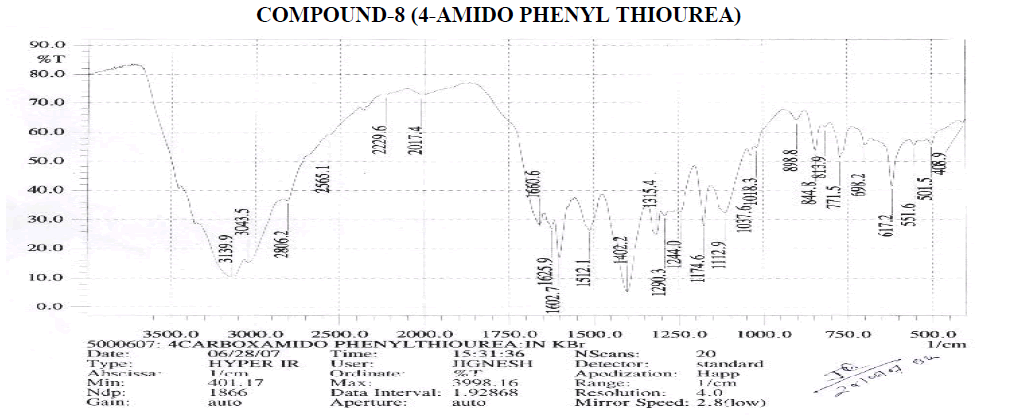
Aromatic
? 3043.5 cm-1 - Aromatic C-H Stretching.
? 1402.2, 1602.7 cm-1 - C=C ring Stretching.
? 698.2, 771.5, 813.9, 844.8, 898.8 cm-1 – Out of Plane C-H Bending (Aromatic).
? 771.5 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Ortho Substituted Benzene.
? 698.2 (One Band) and 771.5 (One Strong Band) cm-1 – Meta Substituted Benzene.
? 813.9, 844.8 (Strong Band) cm-1 - Para Substituted Benzene.
Amines and Amides
? 2229.6 cm-1 – C≡N Stretching.
? 1602.7, 1625.9 cm-1 – N-H Bending Primary Amine or Amide.
? 1512.1 cm-1 - N-H Bending Secondary Amine or Amide.
? 1037.6, 1112.9, 1174.6, 1244 cm-1 – C-N Stretching Aliphatic Amine.
Carboxylic Acid
? 1402.2 cm-1 – C-O-H In-Plane bending.
NMR Spectras (Proton NMR)
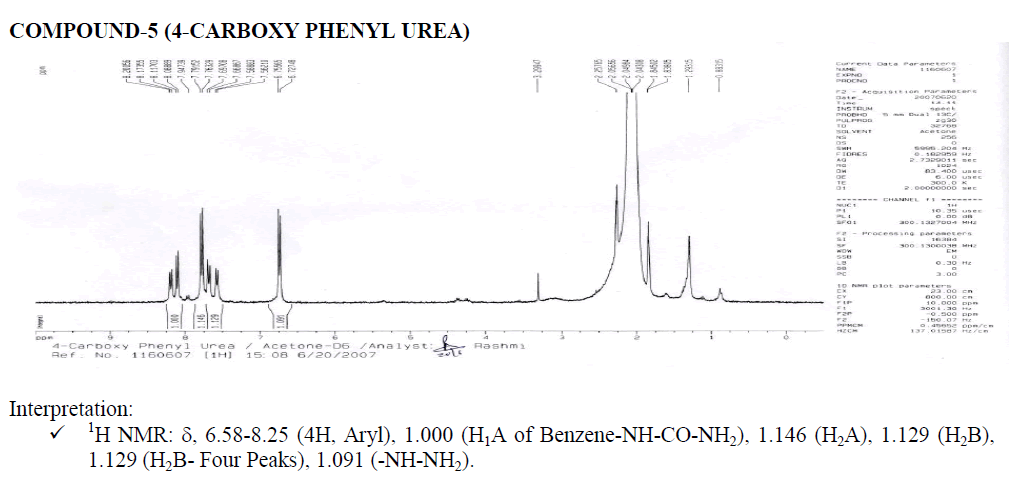
? 1H NMR: ?, 6.58-8.65 (4H, Aryl), 1.000 (H1A of Benzene-NH-CO-NH2), 1.115 (H2A), 2.003 (H2B), 2.003 (H2B- Four Peaks), 1.021 (-NH-NH2).
? Downfield occurs due to –COO group.
Interpretation:
? 1H NMR: ?, 6.58-8.12 (4H, Aryl), 1.000 & 2.074 (Reaction not done Properly), 1.005 (Water of Acetone), ?, 2 (Acetone- Long Peak).
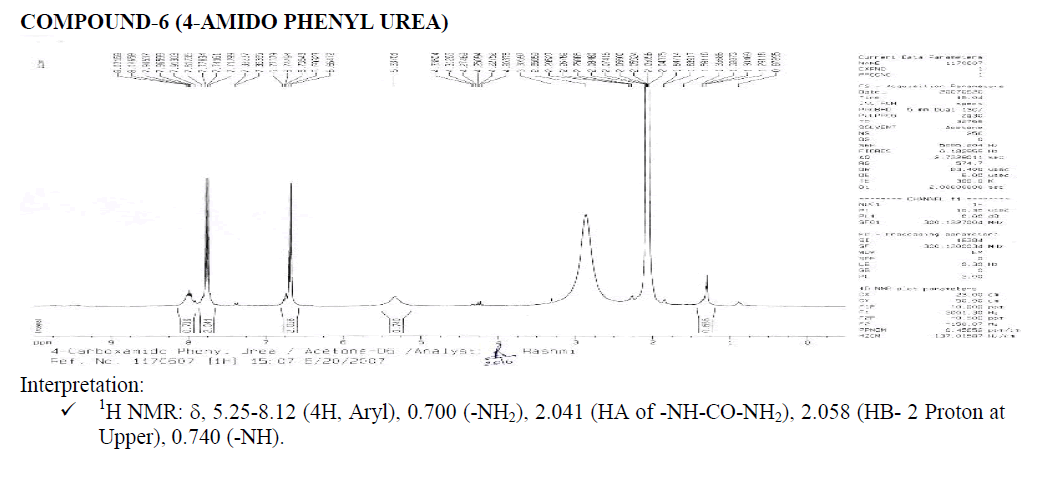
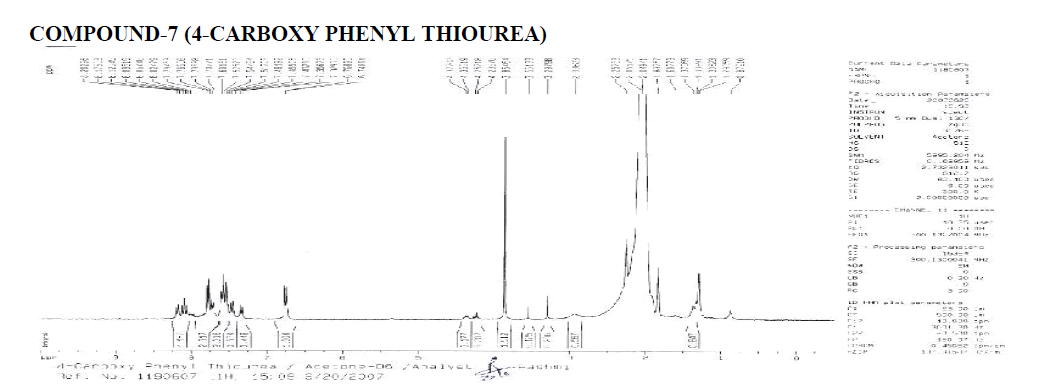
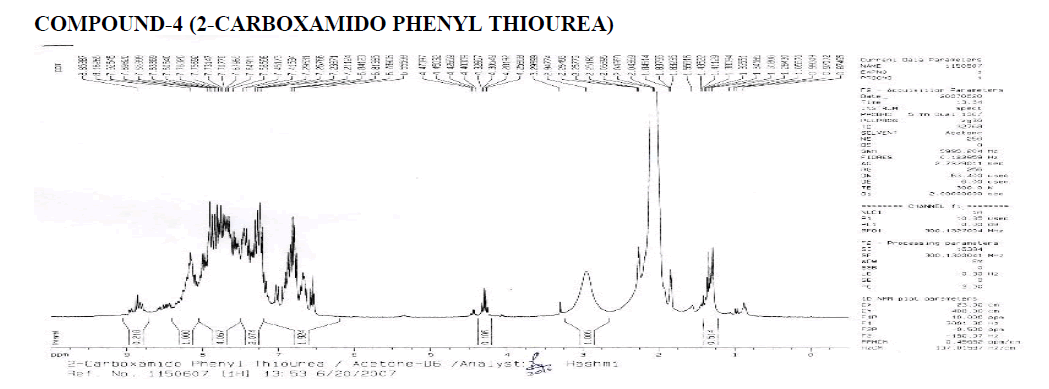
Interpretation:
? 1H NMR: ?, 6.58-8.25 (4H, Aryl), 1.000 (H1A of Benzene-NH-CO-NH2), 2.017 (Aromatic Doublet), 2.016 (Aromatic Triplet).
1.515 (Water of Acetone).
Pharmacological Work[13]:
Acute Toxicity:-
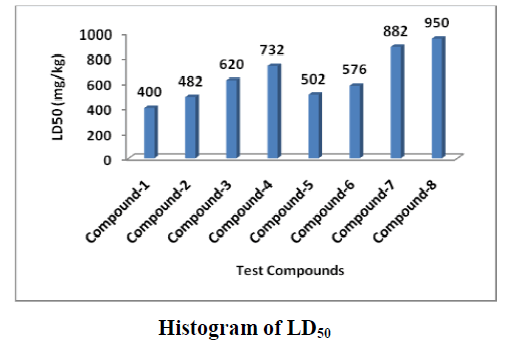
The acute toxicological studies of the compounds were done by determination of LD50 intraperitoneally by mg/kg dose in propylene glycol in 18 hours fasting mice and found that LD50 was as follows in between 400-950 mg/kg, which shows that thiourea derivatives are more toxic than urea linkages and 2-substituted derivatives are lesser than 4-substitition as bond energy in ortho is higher than para substitution:
Compound-1 < Compound-2 < Compound-5 < Compound-6 < Compound-3 < Compound-4 < Compound-7 < Compound-8
CNS Depression Studies:-
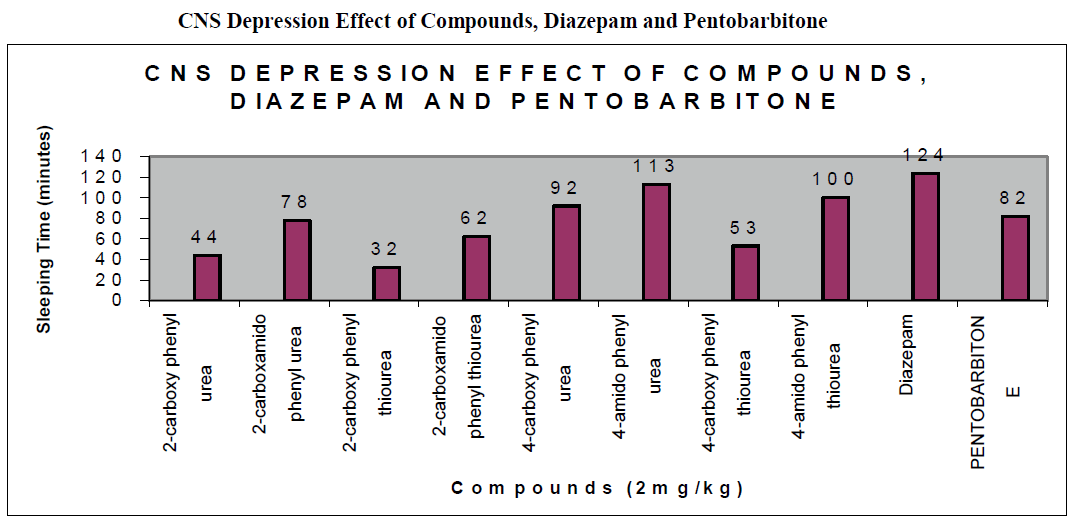
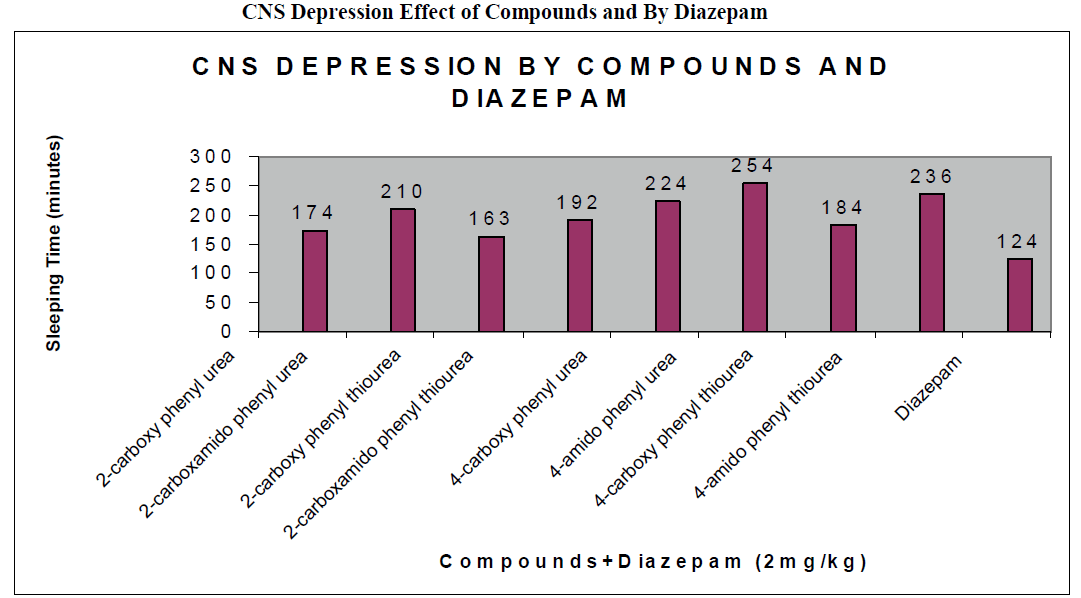
The CNS depression study of all the synthesized compound were carried out by administering intraperitoneally the various doses of the test compounds in mg/kg dose in 18 hours fasting male albino mice using propylene glycol as an inert vehicle. The loss of righting reflex and regaining of it was noted for each compound to determine the sleeping time. It has been found that all the test compounds have sleep inducing property due to the presence of urea/thiourea linkage and the urea/thiourea diamide derivatives were found longer duration of sleep inducing property due to the presence of two amide linkages and out of which the thiourea derivative and thiourea diamide derivatives showed lesser duration than urea and urea diamide linkage. Sleeping time potentiation effect was studied for the test compounds by using pentobarbitone as barbiturates and alprazolam as benzodiazepines on male albino mice. The 2- sustituted derivatives were found less active than 4- substituted derivatives due to the steric hindrance and ortho effect. All the observations were noted for four groups of mice and the bioassay result was tabulated after statistical parameters for significance of pharmacological screening: Student's-t-test and P-value. All the test results were found significant to a high extent for the structure activity relationship studies of the synthesized molecules and the maximum activity has been shown by the COMPOUND-6 (4-Amido phenyl urea) having two amide group[14-16].
Pharmacological Screening:
CNS depression studies have been done on male albino mice (25-35 gms) in 18 hours fasting condition. The test compounds and the standard drugs have been administered intraperitoneally in propylene glycol medium in six groups of animals and biological response has been tabulated in minutes ± SE (Standard Error) for statistical parameters[17]. Student’s-t-test have been recorded and P-value has been determined for the authenticity of the pharmacological response and that has been found satisfactory: P < 0.001%= a; P < 0.01%= b; P < 0.1%=c.
| Compounds |
Dose (mg/ kg) |
Sleeping Time (Minutes) ± SE |
Compounds + Diazepam (Minutes) ± SE |
Potentiation (Minutes) ± SE: Diazepam |
Compounds + Pentobarbitone ± SE (Minutes) |
Potentiation (Minutes) ± SE: Pentobarbiton e |
| 2-carboxy phenyl urea |
2 |
44 ± 0.23a |
174 ± 0.65a |
50 ± 0.49b |
130 ± 0.66a |
48 ± 0.32a |
| 2-carboxamido phenyl urea |
2 |
78 ± 0.31c |
210 ± 0.39c |
86 ± 0.65a |
167 ± 0.21b |
85 ± 0.34a |
| 2-carboxy phenyl thiourea |
2 |
32 ± 0.64b |
163 ± 0.92a |
39 ± 0.46a |
121 ± 0.49a |
39 ± 0.56c |
| 2-carboxamido phenyl thiourea |
2 |
62 ± 0.58 a |
192 ± 0.24b |
68 ± 0.78b |
154 ± 0.12a |
72 ± 0.47a |
| 4-carboxy phenyl urea |
2 |
92 ± 0.43 a |
224 ± 0.47a |
100 ± 0.45a |
183 ± 0.13b |
101 ± 0.36b |
| 4-amido phenyl urea |
2 |
113 ± 0.21 b |
254 ± 0.87c |
130 ± 0.42c |
200 ± 0.34a |
118 ± 0.47b |
| 4-carboxy phenyl thiourea |
2 |
53 ± 0.86b a |
184 ± 0.54c |
60 ± 0.42 b |
127 ± 0.46b |
45 ± 0.76b |
| 4-amido phenyl thiourea |
2 |
100 ± 0.12 c |
236 ± 0.35b |
112 ± 0.76c |
191 ± 0.76b |
109 ± 0.77a |
| Diazepam |
2 |
124 ± 0.25 a |
---- |
|
|
|
| Pentobarbitone |
2 |
82 ± 0.64 a |
---- |
|
|
|
Table 4
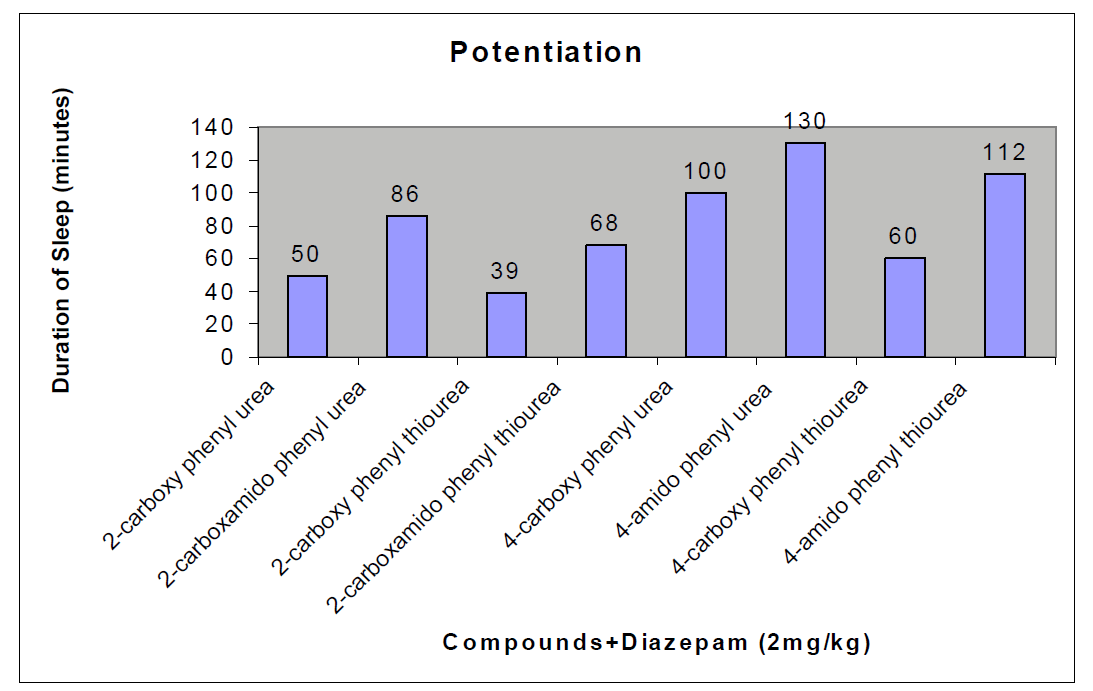
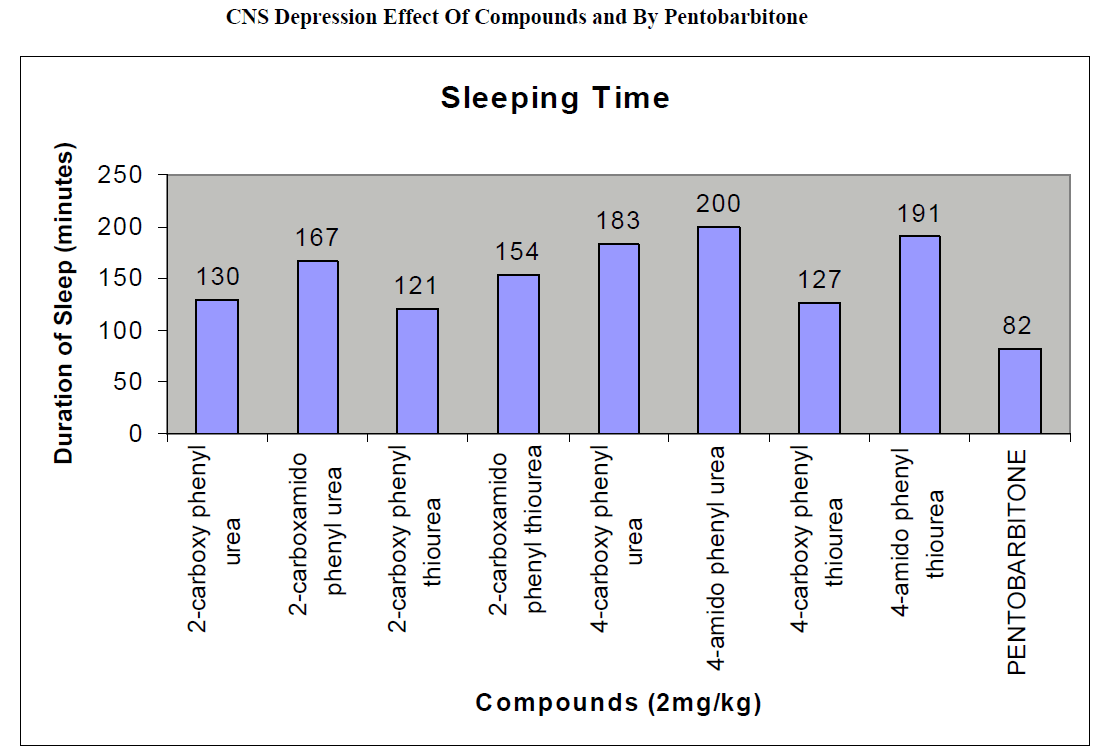
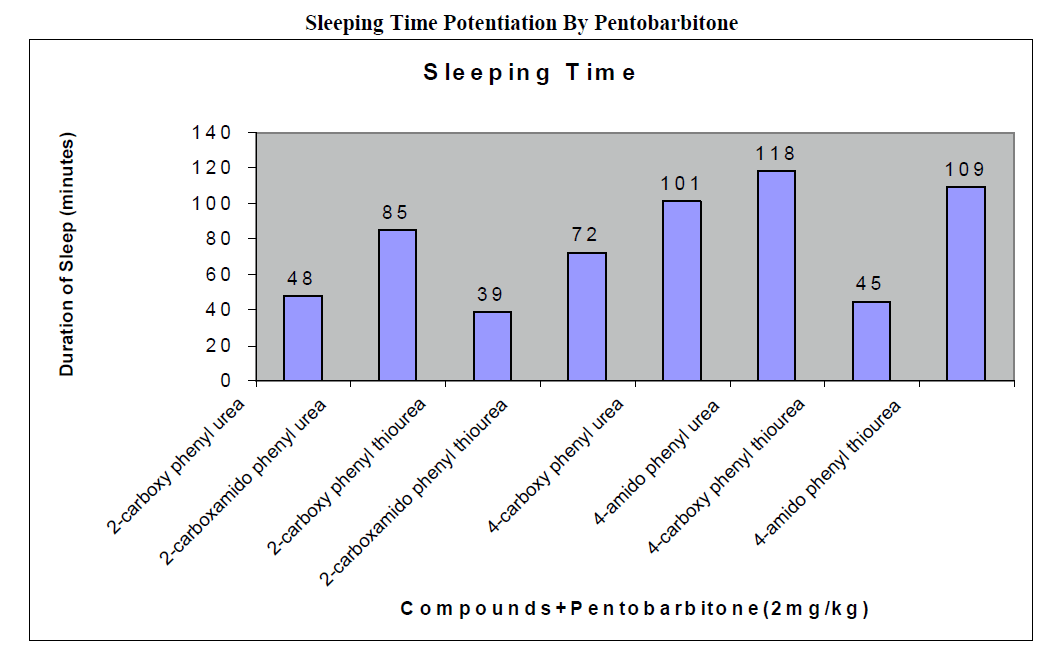
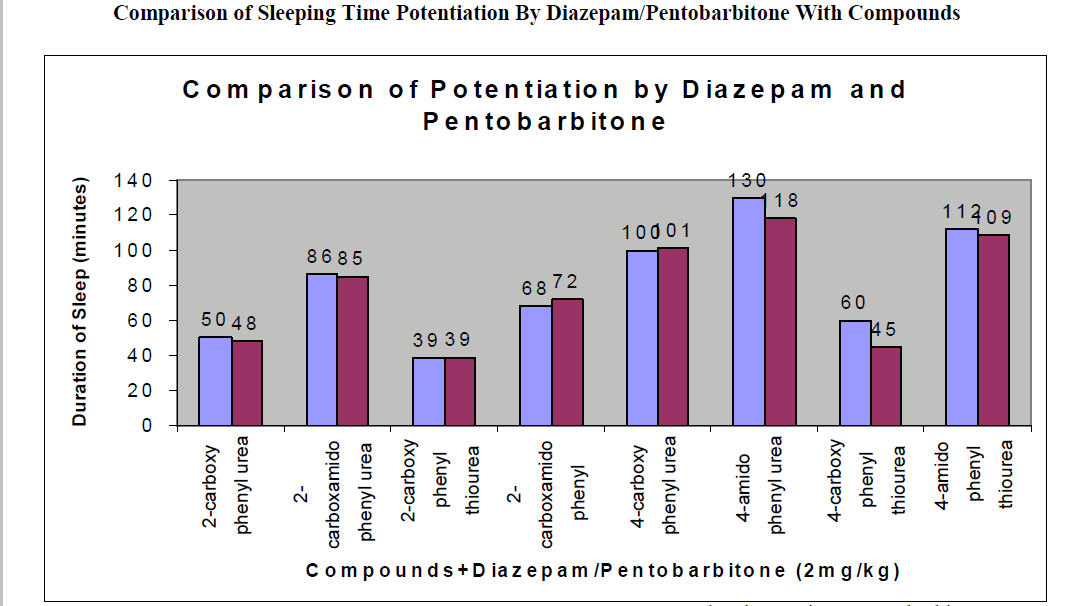
Conclusion:-
It has been found that all the test compounds have sleep inducing property due to the presence of open chain urea/thiourea linkage and the urea/thiourea diamide derivatives were found longer duration of sleep inducing property due to the presence of two test compounds by using pentobarbitone as barbiturates and diazepam as benzodiazepines on male albino mice. The 2-sustituted derivatives were found less active than 4-substituted derivatives due to the steric hindrance and ortho effect. All the observations were noted for four groups of mice and the bioassay result was tabulated after statistical parameters for significance of pharmacological screening: Student's-t-test and P-value. The CNS depression occurs due to the action on GABA receptor having free NH2 and COOH groups: H2NCH2- CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH (ã-amino butyric acid). The synthesized compounds which have free – C(O/S)-NH2 (urea/thiourea) groups and –COOH groups shows the CNS depression effect and the maximum activity has been shown by the compound-6 in which amido as well as urea.
linkages are in para position to each other which blocks the GABA receptor and results CNS depression. The same attachment shows lesser action in case of ortho substitution due to ortho effect and steric hindrance.
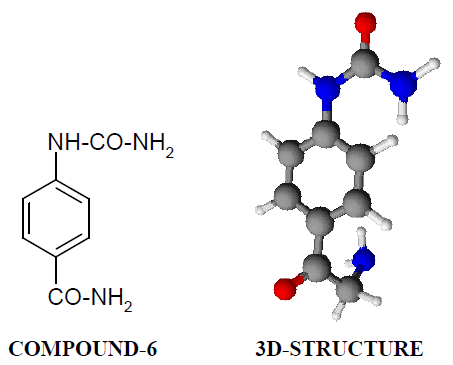
All the test results were found significant to a high extent for the structure activity relationship studies of the synthesized molecules and the maximum activity has been shown by the COMPOUND-6 (4- Amido phenyl urea) having two amide groups.
Acknowledgement:- The author Ravi V. Modi is thankful to the project guide Prof. Dr. Dhrubo Jyoti Sen for successfully finishing this project during M.Pharm. Degree course in Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance specialization under his novel guidance at Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy College, Mehsana, Gujarat and this project has been presented by the author in International Conference on 4th International Congress of Nanotechnology, Sponsored by: International Association of Nanotechnology at San Francisco, United States of America, 5-8 November 2007. The author is also thankful to Quality Assurance Department of Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy College, Mehsana, Gujarat for UV and IR spectral datas, thankful to Oxygen Healthcare, Ahmedabad, Gujarat for Mass Spectral datas and thankful to Panjab University, Chandigarh for NMR spectral datas.
Conflict of Interest: Project guide-Prof Dr Dhrubo Jyoti Sen
Source of Support: Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy
Author Information: Ravikumar V. Modi did this project under the guidance of Prof Dr Dhrubo Jyoti Sen at Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy College, Mehsana, Gujarat during his M.Pharm. Degree course (2005-2007) and at present Mr. Modi is a final year student of MBA in USA.
5344
References
- Carrie L. Randall and David Lester (2002);nJournal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics,n88(2), 1073-1076.
- Leagendre R and Pieron H (1910), ChemicalnRoyal Society of Biology, 68, 1077.
- Prabhu G.V. and Venkappayya D., (1995),nJ.Indian Chem.Soc., 72, 681-684.
- Dandiya P.C., Sharma P.K. and Menon M.K.n(1962): Ind. J. Med. Res., 50, 752-760.
- A.I. Vogel, Vogel's Textbook of PracticalnOrganic Chemistry 3rd Edition (1956), Longmans, Greennand Co Ltd, London, p:280-310.
- Misra A.K., Dandiya P.C. and Kulkarni S. K.n(1973): Ind. J. Pharmac. 5, 449-450.
- Turner, R.A.(1965). Depressants of the centralnnervous system. In Turner, R.A. (Ed) Screening methodsnin pharmacology, Academic Press, New York and London,npp. 69-86.
- Singh J., Khosla P., Srivastava P.K. (2000),nNimodipine potentials anesthetic effects of ethanol pentobarbitone and ketamine in rats. Indian J Pharmacol;n32: 206209.
- Ghosh M.N., Fundamentals of ExperimentalnPharmacology, 2nd edition, (Scientific Book Agency,nCalcutta), 1984, p: 153-157, 190.