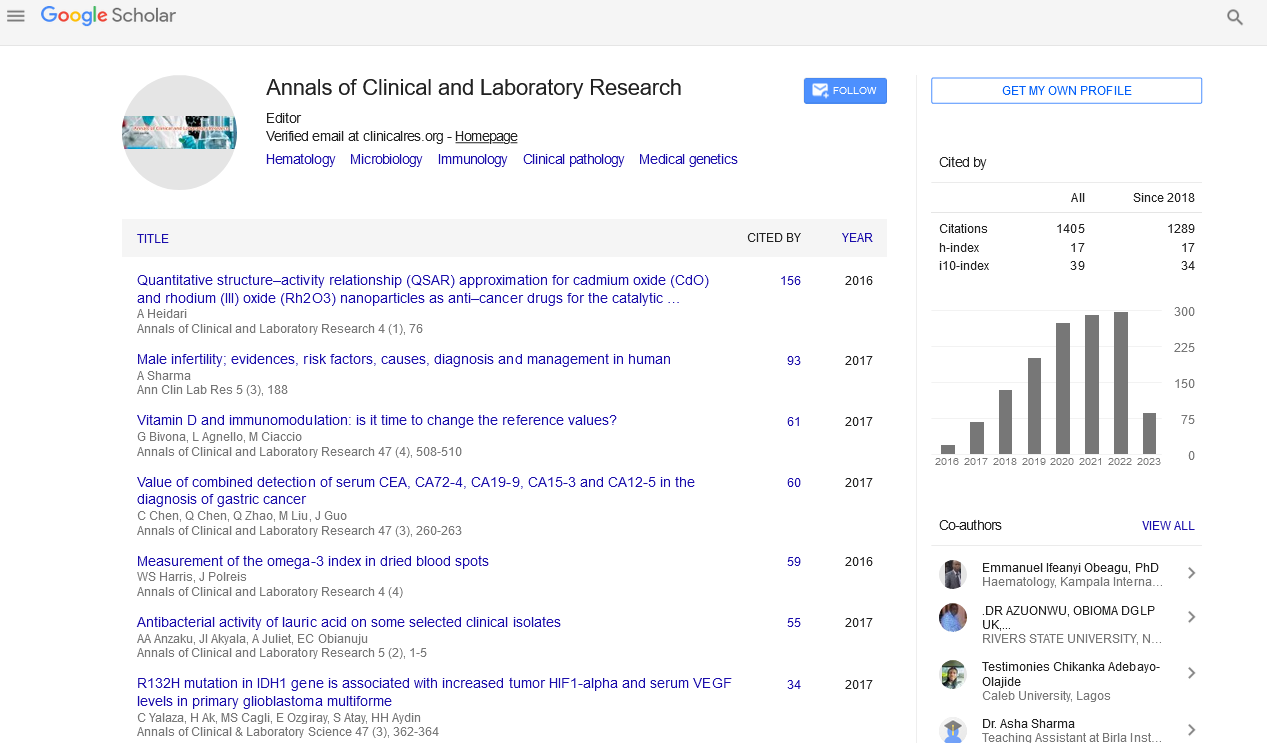
Prospective - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 2
Tending to Wellbeing Proficiency
Responsiveness in Diabetes
Daniele Mannucci
1Department of Diabtology, Careggi Hospital, Italy
Received: 10-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. IPACLR-22-399;
Editor assigned: 11-Jan-2022, Pre QC No. IPACLR-22-399(PQ);
Reviewed: 31-Jan-2022, QC No. IPACLR-22-399;
Revised: 21-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. IPACLR-22-399(R);
Published:
28-Feb-2022, DOI: 10.36648/2386-5180.22.10.399
Abstract
Diabetes trouble is a significant long haul challenge for people, networks, administrations and frameworks. Tending to wellbeing proficiency is a key supporting issue of wellbeing imbalances and to illuminate administrations and arrangements in producing proper reactions to the necessities of individuals with diabetes. The idea of wellbeing proficiency has developed from essential useful abilities in perusing and numeracy to a multi-layered one including the capacities and assets with respect to access and openness to wellbeing data and administrations to keep up with great wellbeing considering the different settings of people. The significance of wellbeing education is appropriate given the present need to coordinate the developing computerized attack and the dire requirement for educated and open collaborations with media and administrations (eHealth proficiency). Thusly, medical care administrations and suppliers, as well as strategies and leaders need to perceive and adapt to assorted wellbeing education needs, particularly for the most powerless. A few promising advancement projects are on-going in Europe and worldwide to address wellbeing (and eHealth) proficiency for the co-plan and increasing of possibly maintainable mediations and strategies with respect to the anticipation and the administration of diabetes.
Keywords
Diabetes, Medicine, Asymptomatic
Introduction
Diabetes, likewise with numerous non-transmittable constant
infections, is chiefly asymptomatic, however opens individuals
to long haul entanglements. The board of diabetes is trying as it
principally requires preventive instead of remedial perspectives
and preparing numerous assets and suppliers. In diabetes, the
two patients and medical care suppliers are gone up against in
reality with the everyday and long haul the executives of the
sickness.
Wellbeing education alludes to the mental and interactive
abilities that decide the capacity of people to get to, comprehend,
recollect and involve data in manners that advance and keep
up with great wellbeing [1]. Wellbeing education is a possible
determinant in achieving way of life conduct, drug adherence,
and sufficient observing of constant infections. Wellbeing
proficiency has been connected to numerous wellbeing pointers
and results and is a possible key part of wellbeing insights and
practices.
Wellbeing proficiency has for some time been decreased
to simply proficiency (perusing and composing abilities and
hardships) as applied to wellbeing data, and has been connected
to schooling level, age, work and pay level. In any case, past this
utilitarian education, intuitive and basic proficiency is fundamental.
Intelligent wellbeing proficiency abilities incorporate the complex
mental and interactive abilities expected to do ordinary exercises,
to extricate data and construe significance from various types of
correspondence, to apply new data to changing conditions and to
interface with wellbeing administrations. Basic proficiency alludes
to the abilities that can be applied to dissect basic data and adjust
to adapt to life circumstances. Additionally, the multi-faceted
parts of wellbeing education must be recognized, to evaluate the
requirements and difficulties of individuals and to be responsive
concerning access, openness, and reasonableness, of wellbeing data
as well as wellbeing administrations and suppliers [2]. Wellbeing
education responsiveness alludes to how wellbeing laborers and
the frameworks around them perceive and oblige to the wellbeing
proficiency needs of the local area so fair admittance to and
commitment with wellbeing data and administrations is streamlined.
Many apparatuses to survey wellbeing education have been
created. The first, and up to this point, the most often utilized, are
the Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine (REALM), Test
of Functional Health Literacy in Adults (TOFHLA), Newest Vital
Sign (NVS), which surveyed perusing and perception abilities,
as well as numeracy abilities. Later apparatuses have been
created to catch the full scope of aspects exemplified in the full
idea of wellbeing proficiency. The multi-faceted Health Literacy
Questionnaire (HLQ) was created on the hypothetical premise
of the World Health Organization (WHO) meaning of wellbeing
proficiency, and its development followed a thorough grounded
legitimacy driven approach [3]. The applied turn of events and
the mental testing of the things profited from broad patient and
suppliers investment. The HLQ, utilized in north of 60 nations and
deciphered in excess of 40 dialects (Richard Osborne, individual
correspondence), has powerful psychometric properties and
investigates wellbeing education through nine discrete and
autonomous theoretical scales: Feeling got it and upheld by
medical care suppliers; Having adequate data to deal with my
wellbeing; Actively dealing with my wellbeing; Social help for
wellbeing; Appraisal of wellbeing data; Ability to effectively
draw in with medical care suppliers; Navigating the medical
care framework; Ability to track down great wellbeing data;
Understanding wellbeing data alright to know what to do. These
furnish experts and program administrators with helpful data
about what is happening for gatherings of local area individuals
and data on what is expected to further develop wellbeing
administrations [4].
Critically, electronic wellbeing (eHealth) proficiency must be
thought about as well. As wellbeing administrations keep on
preparing advanced instruments, the capacity 'to look for, find,
comprehend, and assess wellbeing data from electronic sources
and apply the information acquired to tending to or tackling a
medical issue' is turning out to be progressively basic. Devices
have been created to evaluate eHealth proficiency, like the
eHEALS, and the multi-faceted eHLQ, which envelop the different
spaces of eHealth education, needs [5].
REFERENCES
- Osborne RH, Batterham RW, Elsworth GR, Hawkins M, Buchbinder R (2013) The grounded psychometric development and initial validation of the Health Literacy Questionnaire (HLQ). BMC Public Health 13: 658.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Greenhalgh T (2015) Health literacy: towards system level solution. BMJ 350: h1026.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- D. Nutbeam (2008) The evolving concept of health literacy. Soc Sci Med 67: 2072-2078.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Batterham RW, Hawkins M, Collins PA, Buchbinder R, Osborne RH (2016) Health literacy: applying current concepts to improve health services and reduce health inequalities. Public Health 132: 3-12.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
- Debussche X, Lenclume V, Balcou-Debussche M, Alakian D, Sokolowsky C, et al. (2018) Characterisation of health literacy strengths and weaknesses among people at metabolic and cardiovascular risk: validity testing of the Health Literacy Questionnaire. SAGE Open Med 6:2050312118801250.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Citation: Mannucci D (2022) Tending to
Wellbeing Proficiency Responsiveness in
Diabetes. Ann Clin Lab Res. Vol.10 No.2:399