Jia Yu Wang1, Chen Chen Jiang2, Xu Guang Yan1, Lei Jin2* and Xu Dong Zhang1*
1School of Biomedical Sciences and Pharmacy, University of Newcastle, NSW, 2308, Australia
2School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Newcastle, NSW, 2308, Australia
Corresponding Author:
Xu Dong Zhang
Room LS3-49, School of Biomedical Sciences and Pharmacy
Life Sciences Building, University of Newcastle, Callaghan, NSW 2308, Australia
Tel: 61 2 49218906
Fax: 61 2 49138184
E-mail: Xu.Zhang@newcastle.edu.au
Lei Jin
School of Medicine and Public Health
Life Sciences Building, University of Newcastle
Callaghan, NSW 2308, Australia
Tel: 61 2 49218906
Fax: 61 2 49138184
E-mail: Lei.Jin@newcastle.edu.au
Received date: 21 July 2016; Accepted date: 25 July 2016; Published date: 30 July 2016
Citation: Wang JY, Jiang CC, Yan XG, et al. TH588 Potently Kills Melanoma Cells Grown in 3-Dimensional Culture Through Apoptosis Induced by ROS. Arch Can Res. 2016, 4:3.
3D Culture Performed Using the Hanging Drop Technique
MutT homolog 1 sanitizes oxidized dNTP pools through converting 8-oxo-deoxy-guanine (8-oxo-dGTP) and 2-OHdeoxy- adenosine (2-OH-dATP) into the corresponding monophosphates, thus protecting cells from DNA damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
As one of the first-in-class MutT homolog 1 (MTH1) inhibitors, TH588 has been reported to kill cancer cells leading to impressive therapeutic responses in various human cancer xenografts [1]. However, our resent results and those reported by others have raised concerns about the potential of MTH1 as therapeutic target and the specificity of TH588 as a MTH1 inhibitor [2-4]. Nevertheless, our results demonstrating TH588 kills melanoma cells but did not impinge on the survival of melanocytes suggest that it remains a promising candidate for melanoma treatment [2]. Here, we report that TH588 indeed potently kills melanoma cells grown in 3-dimensional (3D) culture, and that is mediated by ROS and is related by activation of the BH3-only protein Bad and down regulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 (Figure 1).
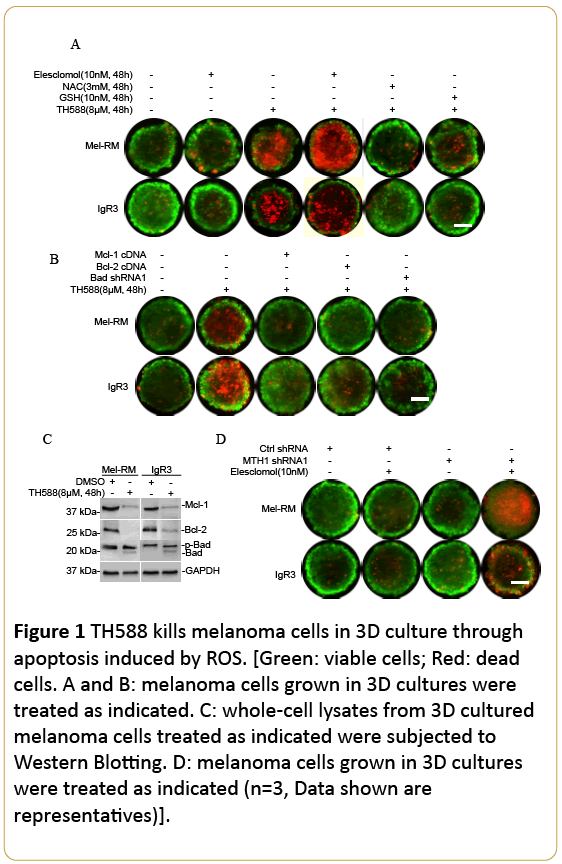
Figure 1: TH588 kills melanoma cells in 3D culture through apoptosis induced by ROS. [Green: viable cells; Red: dead cells. A and B: melanoma cells grown in 3D cultures were treated as indicated. C: whole-cell lysates from 3D cultured melanoma cells treated as indicated were subjected to Western Blotting. D: melanoma cells grown in 3D cultures were treated as indicated (n=3, Data shown are representatives)].
3D culture was performed using the hanging drop technique as previously described [5]. Cells were stained with calcein AM and ethidium homodimer-1 for 24 h followed by the treatment.
9956
References
- Gad H, Koolmeister T, Jemth AS (2014) MTH1 inhibition eradicates cancer by preventing sanitation of the dNTP pool. Nature 508: 215-221.
- Jiayu W, Lei J, XuGuang Y (2016) Reactive oxygen species dictate the apoptotic response of melanoma cells to TH588. JID 16: 32104-2.
- Petrocchi A, Leo E, Reyna NJ (2016) Identification of potent and selective MTH1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med ChemLett 26:1503-1507.
- Kettle JG, Alwan H, Bista M (2016) Potent and selective inhibitors of MTH1 probe its role in cancer cell survival. J Med Chem59(6):2346-2361.
- Tay KH, Liu X, Chi M (2015) Involvement of vacuolar H(+)-ATPase in killing of human melanoma cells by the sphingosine kinase analogue FTY720. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 28:171-183.