Research - (2023) Volume 17, Issue 3
Reflective Practises In Health Care Profession
Olaniyi Ogundiya Phd1* and
Okhiai Okhemukhokho2
1Federal College of Education, Oyo School of Secondary Education (Science Programmes) Physical and Health Education Department, Nigeria
2College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Sciences, Ikeji Arakeji, Osun State, Nigeria
*Correspondence:
Olaniyi Ogundiya Phd, Federal College of Education, Oyo School of Secondary Education (Science Programmes) Physical and Health Education Department,
Nigeria,
Received: 16-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. phsj-23-13502;
Editor assigned: 20-Feb-2023, Pre QC No. Iphsj-23-13502 (PQ);
Reviewed: 06-Mar-2023, QC No. Iphsj-23-13502;
Revised: 13-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. phsj-23-13502(R);
Published:
20-Mar-2023, DOI: 10.36648/1791- 809X.17.3.1001
Abstract
This article explains the roles of reflective practices in health care profession and its
significant impact in improving the practitioners' skills in reviewing how they have
managed the situation that have occurred most especially how they have identified
various areas in health profession that required further developments. It further
explains in detail the meaning of reflective practises in health and social care and
underscores its impact on the roles of reflection practice in health care services, the use
of the practice theme as a framework for reflection, demonstration of active, ongoing
critical reflection of learning experiences and assessment of the overall success of own
reflective journey with the consideration of future carrier partway. It finally concludes
that reflective practises encourage the health practitioners to holistically examine the
health problems of the service users daily, providing skillful approaches through critical
reflection to understand the aetiology of the health problem and develop reflection
of working practises to overcome the health challenges. It finally recommends that
reflective practises should be encouraged among the health care professionals and
should be included in the curriculum as an integral part of the nursing education in
order to facilitate the optimum healthy living of both the staff and the concerned
service users.
Introduction
It has been observed that health care professionals especially nurse face a lot of challenges and frustration when dealing with their patients in the wards. Responding to patent’ needs especially the one in critical situation and vulnerable individuals, the practitioners experience various difficulties in the stressful environment. Reflective practises explicitly consider the emotional impact that both the duo encounter in the process of a care delivery (Nurses& patent or service users) have on each other during the course of the health care activities. It also involves what the health practitioners can learn and observe from their thought and feeling instead of being denied or discounted [1]. However, their thought and feeling are valued and are critically examined to explore new insight that will inform future works. This leads to the question, what is refection practises and its roles among the health professionals?
Definition of Reflective Practices
Reflection could be identified as a way of examining and considering the thoughts, reactions of oneself and others to a given situation or happenings or events to holistically understand the situation at hand and to proffer more systematic and effective ways of responding in future. It enables the practitioner developing critical thinking, understanding the immediate health needs and approaches to patient care. It also gives room for the promotion of self - awareness, effective communication skills and relationship with the service users. However, to be an effective reflector, it requires being prepared to uncover one owns perception and to be objective about these perception and subsequent judgments may have affected one‘s chosen perception. Furthermore, reflection should be seen as a way of learning about ourselves, environment and colleagues in such a way that the result could be implemented to improve the health and well-being of both the reflectors and the service users in the health care profession and practises. Reflection helps us to understand what has gone wrong or well.
Reflective Practises in nursing profession
The practice of reflective practises is very common in nursing profession because of the nature of the care provided and the nurse’s commitment to work and high emotional cost of their daily duties. Reflective practices are assumed to be part of health care profession and its nature and evolution is well documented [2-4], It is a key element of continuing professional development and part of the Nursing and midwifery council revalidation requirements (NMC, 2015) Nurses experience trauma and exhibit human vulnerability in a striking way, witnessing injury and distresses on daily basis. They experience human frailty that could easily relate to themselves or those close to them. Reflective practises allow the total involvement of the nurses in their work and help them to be more focused rather than separating out acceptable and acceptable feelings. It enables the nurses to fully engage with their works and by extension increases their interest, motivation and increases their care of patients and above all, giving them the opportunity to look more closely at themselves in a safe environment and allows them to be more present for their service users and able to meet their needs as at when due. Reflective practises considers the emotional effect nurses and patient have on each other and what the reflector can deduce from their thought and feeling with being examined carefully in order to gain insights to inform future works.
Reflective practices in health care profession could also be regarded as a mean to improving the practitioner’s skills towards ensuring that enviable health care delivery system is achieved in the society. Qualitative health care delivery is a system that promotes the health and well-being of the service users through skillful approach and evaluation of the health care practitioners to understand the health challenges through critical reflection and examination of the aetiology of the health problems. Reflection in health and social care practises among the health workers enables Elliot et al (1999) the practitioners to reflect on the roles regarding learning experiences. Explained that reflexivity in qualitative research is very important and enables the health workers to consider their value, interest attitude and assumption towards their learning experiences. Such as health challenges of the service users. Reflection practises enable the practitioners to effectively work with others, influence and change own and other values, attitude, approaches and behaviors. For instance, challenging hidden assumption.it encourages the health workers to develop an understanding of different perspectives and viewpoints. These viewpoints may be referred to sharing with students, colleagues, strength and preferences and developments [4]. noted that reflective practises by the practitioners enable them to be current with knowledge and practises. For instance, it gives supports to individual to improve and continue the way they work on the quality of care delivered to people. This, however, encourages the practitioners to provide efficient and high- quality services and adopt a more professional approach to the service users. Reflective practises also expand a leaders’ self-awareness, promotes critical thinking and hones communication skills which eventually improve and enable the growth of an organization. Reflecting practises also help to evaluate and revising own practises and influencing organization change. It is important to state that through the consistence practising of reflective practises, successful aspect of our health care delivery is appreciated no matter how small may be. It also allows organization experience and ideals into useable knowledge and action. The use of reflective practises among the health workers cannot be alienated as it promotes personal development and progression in carrier pathway. It creates selfawareness, a key and important component of the emotional intelligence that enables a better and adequate understanding of people [5]. Reflective practices skills and considers reviewing their effectiveness rather than being constantly doing what you are always doing regularly and to see if there is better way of doing it in future. it allows the practitioners to provide assessment of their own thought and action leading to personal development of the practitioners and other people around them especially the service users. Reflective practises are considered as the foundation or fundamental to professional development. It helps to transform insight to practical strategies for personal growth and development. Reflective activities help to develop abilities to comprehend how the students learn. It helps the teacher to identify obstacle during learning experiences. It enables the practitioners having a wider range of skills during teaching. http//www.cambridge-ommunity.org. It also helps to build relationship, health and well-being of the practitioners. The role of reflective practises cannot be underestimated as it helps to promote a high-quality service to the user or the clients and enables the practitioners identify areas for developments where amiable reflective practice can be put in place.
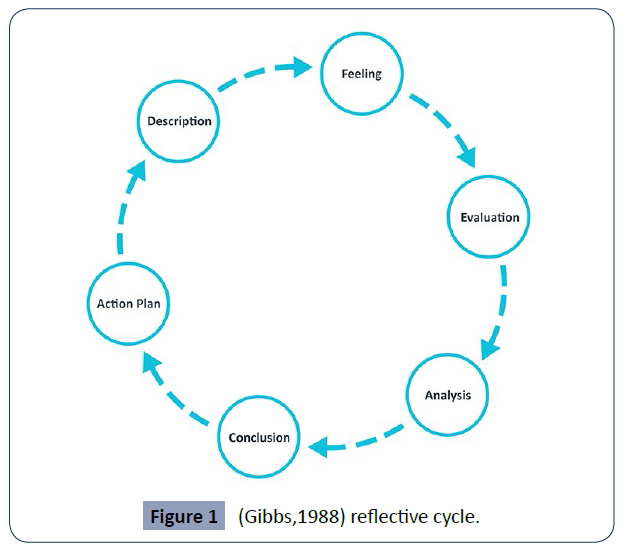
However, it should be noted that when reflection practices are not utilized or put into practices in any organization. it could be more hazardous and the objective of such organization is doomed and unrealistic without any reflection and practices that would encourage more enlightenment and provision current information to improve the organization skills, especially among the health practitioners. The career progression of the practitioners is greatly affected and underdeveloped when the expected skills and knowledge is not available in the reflection of the practices. Also, Lack of good reflective practices could lead to unmotivated workforce and poor quality care in term of giving optimum health care delivery to the service users. Individual can witness various problems regarding psychological health, physical health and safety which may affect the progress of the practitioners’ carrier. (Harris & Mayo, 2018) It is essential to mention that there is need to ensure that knowledge and skills are well updated and consistently reflected upon by the health practitioners. Reflective practises involve the practitioners using self-awareness, description, critical analysis, synthesis and evaluation. (Atkins& Murphy, 1994) These help the practitioners analyzing their own experience to improve their carriers. Gibb (1998) reflective circle explains the six stages that it encourages people to think systematically about the experiences they had during an event, situation using a circles, the reflection could structure in stages. It helps the health practitioners such as nurses to keep space with the changing nature of practises by allowing them to regularly improve their skills (Figure 1).
Figure 1 (Gibbs,1988) reflective cycle.
Reflective cycle comprises six stages which involves description of the incidence that happened, it describes how, when, where, who or what did they say/witness or hear, how did it happen. It describes the circumstances. The second stage is feeling. This involved what the thinking is about? It asks questions about the initial gut reaction. Does that change feeling? What was the thinking you have experienced. It also includes evaluation whether it bad or good experience. What has made it unhappy? What requires improvement? What was helpful or unhelpful? It also analysis. For example, what sense can you make of the situation? It compares theory and practises what are the differences between the experiences. The conclusion describes what have you concluded or leant for the future. Lastly, what action would be in place to rescue the situation? The person or nurses is encouraged to observe closely to the experiences and listen to how they respond internally [6].
Example of reflective practise
I was asked to take complete care of 4 patients in the ward of the tertiary hospital under the supervision of my mentor nurses’ specialist. The night shift new graduate registered nurses (RN) handed over to us that one of our post- operative patients had an indwelling catheter (IDS) Catheter(IDC) which was taken out a night before and patient voided after removal of IDC. The RN reported that patients in continents aid was moderately wet at night, However the patient was still complaining of not being able to void which made RN think that the patient was confused. Upon receiving a handover, I found out that my patient was restless and when asked, she stated she had a lot of pain in her lower abdomen [7]. A quick physical examination revealed distended lower abdomen. After reviewing her clinical notes, I noticed that the patient had received analgesia PRN (as needed) for abdominal pain early that morning however, no further investigation and intervention were conducted to find out the causes of the pain. Furthermore, I assessed the patient and found that she was well oriented to time, place and the patient has no significant history of confusion or delirium in her clinical notes [8, 9].
Feeling: At that time, I felt the situation wasn’t correct and I reported immediately to my mentor. She appreciated my initiation and instructed me to perform an ultrasound bladder scan. (Belous & Fautes, 2013, pp. 62-63)
Practicality of my goals and personal contribution to the teamwork using Cribbs reflective Model
Crib’s reflective Models Reflective models comprises of description, feeling, evaluation, action plan, analysis and conclusion.
Description
Feeling I have set goals that are achievable with considerable good time to contribute. I am always feel happy working in a team and I will be able to contribute my own quota into the team.
Evaluation from my understanding, I think my targets are achievable. The targets are achievable within reasonable time frame. Though, along the lines, there have been various challenges such as language barriers which possibly might have hindered communication flows, notwithstanding, I have added value to the teams such as ethical consideration of works. I have equally learnt and grow in the teams.
Action plan there is need to engage in relevant training to make me more relevant professionally and secure more qualification.
Analysis My job is very important and has been so assistive to help the vulnerable individual and ensure that they receive health care in order to facilitate optimum health living.it right steps to take that will promote the community. it is important as a member of the team to develop myself professionally and ensure that my skills and knowledge are updated so that I can provide adequately the care that meet the needs of the criteria of national standard. By reflecting, I can improve myself to see how things will be done to better the situation Conclusion In conclusion, my plans are realistic and achievable, and I believe it will enable me to practise and develop skills to provide assistance to person -center care and that I am performing well in my work placements.
Tools and Techniques to gather evidence to reflect on practises
According to (Wilson, 2020) describes reflection as an in -depth focused attention and reflective practises as the development of insight and practises through critical attention to practical values, theories, principles, assumption and the relationship between theory and practise which inform every day. The importance of reflection practises in the development of optimum healthy living in health care industry cannot be alienated. It helps the carer to work with and collaborate effectively with other. It also helps in the evaluation and revising own practises; it identifies new opportunities for learning and identifies new course for action. However, it should be noted to practise a successful reflection practise as an individual or in any organisation or in any health care industry, there is need to understand the practical learning and assessment documentation portfolio indicating the means to gather evidence of effective learning and development. This evidence involves induction records, certificate of training and CPD self- learning through internet, media and other sources collaborative action learning group reflection evidence of practise or learning from other unit development plans. It also includes reflective account on learning using own or other modes of reflection narrative and case studies reflection. Gathering evidence to reflect on practise also involves using record of one to one and group appraisal, assessment and feedback from colleague and professionals, family, friend and services user’s records of assessors, observation of practises, work placement, time sheet, and witness testimony are all tools for evidence of the practitioners to reflect on practises.
The use of practise theme as framework for reflection practises
Practise theme refers to the ability to reflect on an individual action in order to engage in a process of continue learning. The use of practise theme in refection involves creating a main theme, brainstorm ideals and learning experiences related to the developed topic and lastly, analysis of why and how the ideals have affected the interpretation of the themes. Practise theme as a framework involves the following: law regulation, and ethical practises. Professional values, altitude and behaviours in health and social care. Health and safety and safeguarding through the life span and how skills and knowledge are demonstrated, valuing and promoting diversity, differences and inclusion. These themes are useful in reflection practise during health care delivery.
Reflection helps to revealing anxieties, error and weaknesses. It also indicates strength and success. It helps the individuals to develop understanding more deeply and to make our intuitive knowledge shareable with others. for instant, reflection could be a very useful tools in learning kolb’ (1984) explained that the process of learning comprises four stages in which one involves “observation” by reflection, one is able to develop skills in self -directed learning with motivation and be able to develop the quality of care. It encourages professional learning development by ensuring that adequate understanding of their own learning and is achieved. for example, a footballer after any match critically thinks about what they did well or badly or why it was done the way they did it and what they can do to improve it. Law is provided to protect individuals when making decision about their healthcare. Legal standards are useful as they help people to understand what they are not allowed to do, whereas ethical standard is primarily based on human principles of right and wrong. In health care industry, following the standard and expectation of roles from the health carrier to the patient in the hospital. The responsibility, case management, supervision and teaching. Personal development and team working. All these are regulated by law. The health carriers are to be mindful of unnecessary bias such as inequality, provision of relevant care plan for the client, avoid discrimination but should be conscious of the following during the care delivery duty. Equality and diversity and quality care procedure. Confidentiality, risk assessment, independence, respect, individuality, dignity, privacy and partnership.
All these are essential in the provision of quality health care delivery. It is essential that client is allowed to make his or her choice and avoid assumption. The people in the care should be politely addressed and allow them to have their rightful position during the health care delivery they should enjoy the same right as when they were living independently. The client has the right to say no and have the right to relationship at this junction, one may have to balance their right against their responsibility. The client being supported should be allowed to make choices, they should be well informed and guided through the provision of relevant information in older to facilitate the right choices. The client being supported deserves privacy. For instance, visitors must ask permission before entering room and there are needs to close the door when performing personal hygiene. The client should be dignified by the career’s attitude and behaviours. The client feels respected when they are dignified and lastly the wishes of the client must be paramount.
Own development in relationship to theme six practises
It is essential that person centred approach is supported to fulfil its objective as this allows organisational policies and legislation perfectly work with the service users. Relevant research will be conducted at the right time and a job-related training would not be left out.For example, care act (2014) explained that the required rules and regulation would be put into practises while training on policies within the health care section would be updated regularly as a practitioner that provides a qualitative health care delivery. Also, Integrity is equally important during the service delivery as it prompts honest disposition of health care services to the users and further ensure that they are not denied of their rightful legal right and that there is no ambiguity or lack of transparent towards the service users. These would be facilitated to support and promote the person cantered approach or vulnerable individuals. (Careers UK, 2014) safeguarding, health and safety policies. It is part of our duty care to investigate any issues relating to safeguarding especially in safeguarding the vulnerable service users from being harmed. This is a core services to protect the children or individual being abused. The training has increased my orizon and skills in promoting health care services and by extension improving my learning experiences.
Valuing and promoting diversity, differences and inclusion
Valuing and promotion of diversity and inclusion is important to encourage individuals’ values and giving rightful choices among the persons centred individuals. It should be noted that a lot of service users are from various backgrounds, cultural orientation, difference religion as a result of this, there is need to ensure that the care is provided is comprehensive and suitable to the needs of the service users without any prejudice. The care practitioner will ensure that the provision is guided and tailored towards optimising the needs of the clients. Inclusion is equally important as this will help to facilitate unethical care plan with the consent of the service users to prevent them from being deprived from their human right and freedom of speech. Diversity should involve inclusion is included (CIPD, 2021)
Communication
Communication is an essential aspect of health and social care. The client’s behaviours and attitude should be well supported and guided to promote quality care and services that ensure the health, safety and well-being of individuals. This could be done though communication. It could be defined as the exchange of information, thought and feelings among people using speech or other means. It is an instrument role of health and social care and it is a core aspect of working relationship. Effective communication is a skill that has a range of benefit. it promotes good relationships with the service users. Service users are likely to have confidence in what the practitioners tell them and develop confidence in their health carrier. It allows the carer to meet and provide for their individual’s needs. However, communicating poorly with service users can have a range of consequence such as the stress level of the client can increase, poor moral of the client etc. According to USA’ institute for health care explained that communication skills help to realise improving health condition of the patient.
In conclusion, refection practise has been described as the process of learning through experience towards gaining new insight of self and practises (Finlay, 2008) it is important to state that reflective practises among the health practitioners gives room for overall evaluation of the health-related activities among health workers to the service users. The reflective process is structured and focused with an aim to improve practises. It can provide significant services and benefit for the staff. It boosts to gain the people confidence and show rewards. Reflective practises should be made as integral aspect of nursing education and should be included in their academic curriculum. This would help them to develop an insight towards ensuring that the needs of the service users are met and by extension, improving on the emotional well-being of the staff being able to cope with the challenging situation during the service delivery. Reflection among the health workers is expected to showcase being part of the information we required for continued registration through the revalidation, continue professional development or continue educational program and requirement. It is also expected that the patient confidentiality is vital and should seek for gain and development rather than identifying people’s details, activity and experience. Care for individual and services delivery improves when teams and groups are given opportunities to explore and reflect on their work together. This interaction often leads to ideals or action that improves care. It is expected that reflective practises should develop to a course of study that would enhance self- development and possibly as part of safety practises and behaviours of the Nurses or health workers.
References
- Velardo S, Elliott S (2018) Prioritizing doctoral students' well-being in qualitative research. Qual Rep 23: 311-318.
Indexed at, Google Scholar
- Harry Mayo (2018) Taking a case study approach to assessing alternative leadership Models in health care. National Library of Medicine. National Center Biotech inform.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
- Wikinson J (1999) Implementing reflective practice. Nursing Standard (through 2013) 13: 36.
Care act, 2014.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
- Morris TH (2020) experiential learning a systematic review and revision of Kolb’s model. Interactive Learning Env 28: 1064-1077.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
- Adair WL, Loewenstein J (2013) talking it through: Communication sequences in negotiation. In Handbook of research on negotiation. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
- Finlay L (2008) Reflecting on Reflective practice.
Google Scholar
- Willson R (2020) What We Know About Planning, Theory, and Reflection. Reflective Planning Practice 13-25.
Google Scholar
- Belousov AB, Fontes JD (2013) Neuronal gap junctions: making and breaking connections during development and injury. Trends in neurosciences 36: 227-236.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
- Luft T, Roughley R (2016) engaging the reflexive self: The role of reflective practice for supporting professional identity development in graduate students. Create Space
Google Scholar
Citation: Ogundiya O, Okhemukhokho O
(2023) Reflective Practises in Health Care
Profession. Health Sci J. Vol. 17 No. 3: 1001.